- Introduction to Tasmanian Giant Crabs and Their Natural Habitat
- Specialized Habitat Requirements in Zoos
- Techniques to Simulate Natural Conditions
- Importance of Colored Lighting for Stress Mitigation
- Conservation Efforts and Public Engagement
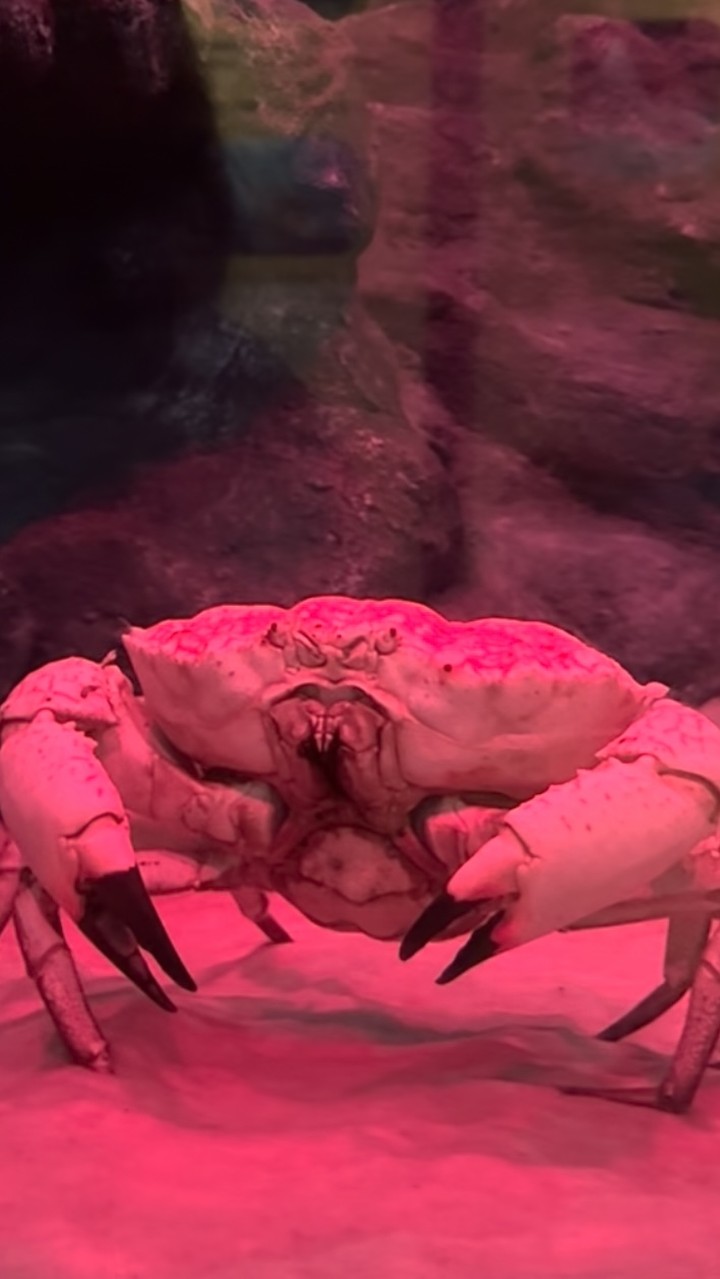
Tasmanian Giant Crabs, scientifically known as Pseudocarcinus gigas, are awe-inspiring marine creatures that captivate the curiosity of marine enthusiasts. Originating in the deep, frigid waters surrounding Tasmania and southern Australia, these crabs thrive in temperatures between 10-14 degrees Celsius. They inhabit ocean depths ranging from 20-820 meters, which are characterized by low temperatures and high pressure. Adapted to such unique environments, Tasmanian Giant Crabs can grow up to 13 kilograms, making them one of the largest crab species.
Creating a sustainable and enriching habitat for Tasmanian Giant Crabs within a zoo setting is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. These crabs require specific environmental conditions to mimic their natural surroundings accurately. To accommodate their need for cold temperatures, zoos employ advanced cooling systems to maintain water temperatures within the range of 10-14 degrees Celsius. Additionally, tanks designed for these crabs are often equipped with substrates that resemble the ocean floor, providing necessary hiding spaces and ensuring their overall well-being.
One significant aspect of maintaining these habitats is regulating water quality. Zoos utilize sophisticated filtration systems that replicate the pristine conditions of the crabs’ native waters. These systems remove waste and control the chemical balance, crucial for the health of the crabs. Routine health checks and monitoring also play a vital role in ensuring the crabs’ longevity and well-being in captivity.
A pivotal part of the exhibit is the use of colored lighting. While natural light, particularly bright white light, can cause stress for Tasmanian Giant Crabs, colored lighting allows for enhanced visibility for guests without disturbing the animals. Blue and green lights are typically used because they closely resemble the wavelengths of light that penetrate deep ocean waters. This lighting setup not only ensures the crabs’ comfort but also provides an aesthetically pleasing and educational experience for visitors.
The introduction of colored lighting also serves an essential educational purpose. Visitors can observe these magnificent creatures in an environment that mirrors their natural habitat. This approach underscores the importance of understanding and respecting wildlife’s needs, emphasizing the significance of creating stress-free environments for animals in captivity.
Conservation efforts are at the heart of showcasing Tasmanian Giant Crabs. Zoos educate the public on the importance of marine conservation by providing an informative and interactive environment. Tasmanian Giant Crabs play a crucial role in their ecosystems as both predators and scavengers, helping to maintain the ecological balance. Highlighting their role in marine ecosystems encourages visitors to support conservation initiatives and adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives.
Moreover, zoos engage in breeding programs to aid the conservation of Tasmanian Giant Crabs. These efforts help to increase the population of crabs in captivity and contribute valuable information to the understanding of their breeding habits and life cycles. Programs like these are vital for preserving the species, especially given the challenges that climate change and human activities pose to their natural habitats.
Public engagement through interactive exhibits and educational programs is key to fostering a sense of stewardship among visitors. By observing Tasmanian Giant Crabs and learning about their habitat requirements, visitors gain a deeper appreciation for marine biodiversity. This engagement extends beyond the zoo as people become advocates for wildlife conservation, supporting policy changes and sustainable practices that protect marine environments.
In summary, the new habitat for Tasmanian Giant Crabs in our zoo is a testament to meticulous planning and dedication to animal welfare and conservation. These magnificent creatures can thrive in captivity by simulating the crabs’ natural environment with advanced technology and thoughtful design. The use of colored lighting not only improves the visitor experience but also ensures the crabs remain stress-free. Through ongoing conservation efforts and public education, zoos play a pivotal role in preserving these remarkable marine animals and promoting a greater understanding of our oceans.
*****
Source Description
Come say hi to our tasmanian giant crabs in their new habitat! 👋🦀
that they thrive in deep, icy cold waters of around 10-14 degrees celcius?🥶 Coloured lighting is used as well to enhance visibility for our guests without causing stress to the animals as they may be overwhelmed by bright white light.