- The importance of veterinary care for aquatic animals, highlighted by the use of x-rays in diagnosing fish health issues.
- Detailed case study of a largemouth bass diagnosed with spondylosis, illustrating fish health management.
- The role of zoo management and veterinary teams in maintaining the health and welfare of aquatic life.
- Conservation and educational insights from treating fish diseases and health conditions.
- Understanding fish buoyancy issues and how modern medicine addresses these challenges.
Fish, often seen as silent inhabitants of aquatic environments, require specialized care, much like their terrestrial counterparts. An intriguing aspect of modern veterinary science is the use of x-rays to diagnose fish health issues. This sophisticated technique is indispensable for detecting internal problems in aquatic creatures that external examination cannot reveal.
A poignant case that brings this to light is that of a largemouth bass that made headlines when it was discovered in distress in December. Observed by its caretakers, the fish was found floating awkwardly, a clear sign of buoyancy trouble. Its skin was drying out due to prolonged exposure to air, a condition that can be life-threatening for fish.
Acting quickly, the veterinary team transferred the largemouth bass to a hospital tank, providing immediate care. This intervention aimed to stabilize the fish, allowing it some respite and the chance to recover from its disturbed buoyancy. Within weeks, the bass showed marked improvement and could comfortably rest at the tank’s bottom, maintaining its balance more effectively—strong indicators of recovery.
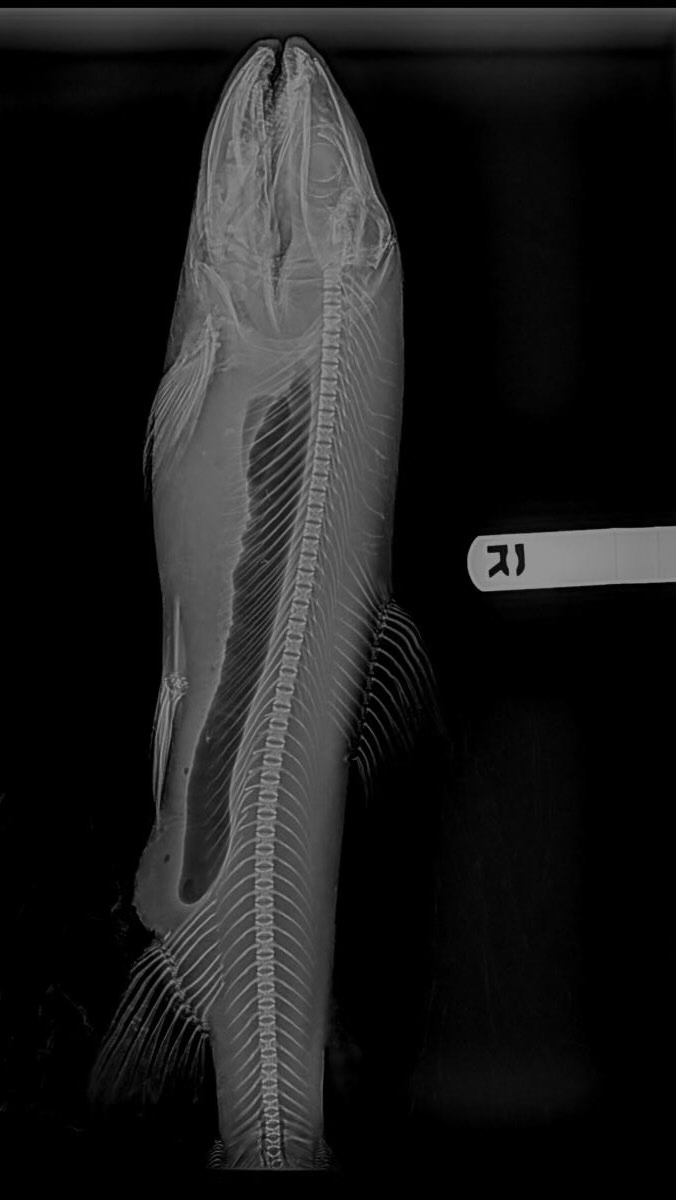
Upon observing these positive changes, the veterinary team deemed it safe to conduct further examinations. They decided to use x-rays to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the fish’s internal condition. This diagnostic tool plays a crucial role in fish healthcare, revealing internal anatomy and potential issues that are invisible externally.
The results of the x-ray examination unveiled that the largemouth bass was afflicted with spondylosis, a degenerative condition of the spine. This ailment, common in aging fish, directly influenced the fish’s buoyancy, explaining the floating episode that prompted its medical intervention. Spondylosis is a progressive disease that requires ongoing monitoring and sometimes treatment to manage its impacts on an animal’s quality of life.
Zoo management, in collaboration with their veterinary teams, plays a pivotal role in the care and upholding of aquatic life well-being. By diagnosing and treating conditions like spondylosis, they ensure that fish like the largemouth bass can live out their lives in comfort and health. This is crucial not just for the individuals involved but for conservation and educational purposes as well.
Fish buoyancy issues are among the many health challenges faced by aquatic creatures. These problems can stem from a range of causes, including infections, physical injuries, or internal complications like organ compression by tumors or growths. Spondylosis is a particular concern since it impacts the spine, a central component in a fish’s buoyancy and movement systems.
Veterinary interventions, including the use of x-rays, underscore the importance of advanced healthcare in zoo management. These practices also illuminate the broader field of wildlife conservation, highlighting progress in understanding and treating conditions that affect diverse animal populations.
The largemouth bass returned to its exhibit, under close monitoring, illustrating a successful intervention by a dedicated team. This story serves as a reminder of the technological and medical advances made in zoological sciences, empowering conservation initiatives and educational outreach.
This tale of recovery and ongoing care not only reflects the dedication of animal care teams but also enhances public awareness about the complexities of fish health. Through such cases, the public gains insight into the intricacies of aquatic animal management, fostering a deeper appreciation for the environments and animals within our care.
The advancements in veterinary science, such as the application of x-ray technology in fish health care, are vital for ongoing conservation efforts. These developments enable better care for individual animals and contribute significantly to ecological balance and biodiversity preservation.
This forward-thinking approach is emblematic of a broader movement towards sustainable and respectful interaction with the natural world. As we expand our knowledge and bolster our capabilities, the importance of caring for and respecting all living creatures becomes abundantly clear. The treatment of the largemouth bass is just one example of the commitment to animal welfare that guides modern zoos and aquariums in their mission to support and educate.
*****
Source Description
Did you know that fish get x-rays?
In December, a largemouth bass was discovered by its keepers, floating with its back exposed above the water and its skin dried out.
The fish was then brought to the hospital tank for further care and observation. After settling into the hospital tank, its buoyancy issues improved, and it was able to maintain a comfortable position at the bottom.
Two weeks later, the veterinary team conducted a follow-up to assess the fish’s progress and found that the bass showed signs of improvement, and stable enough to undergo x-rays.
The results revealed the fish had spondylosis, a condition where the spine deteriorates with age, and likely caused the buoyancy issues.
The veterinary team cleared the bass to return to its exhibit tank, where it will continue to be monitored closely. We’re excited to see the bass recovering and back on track!