Overview
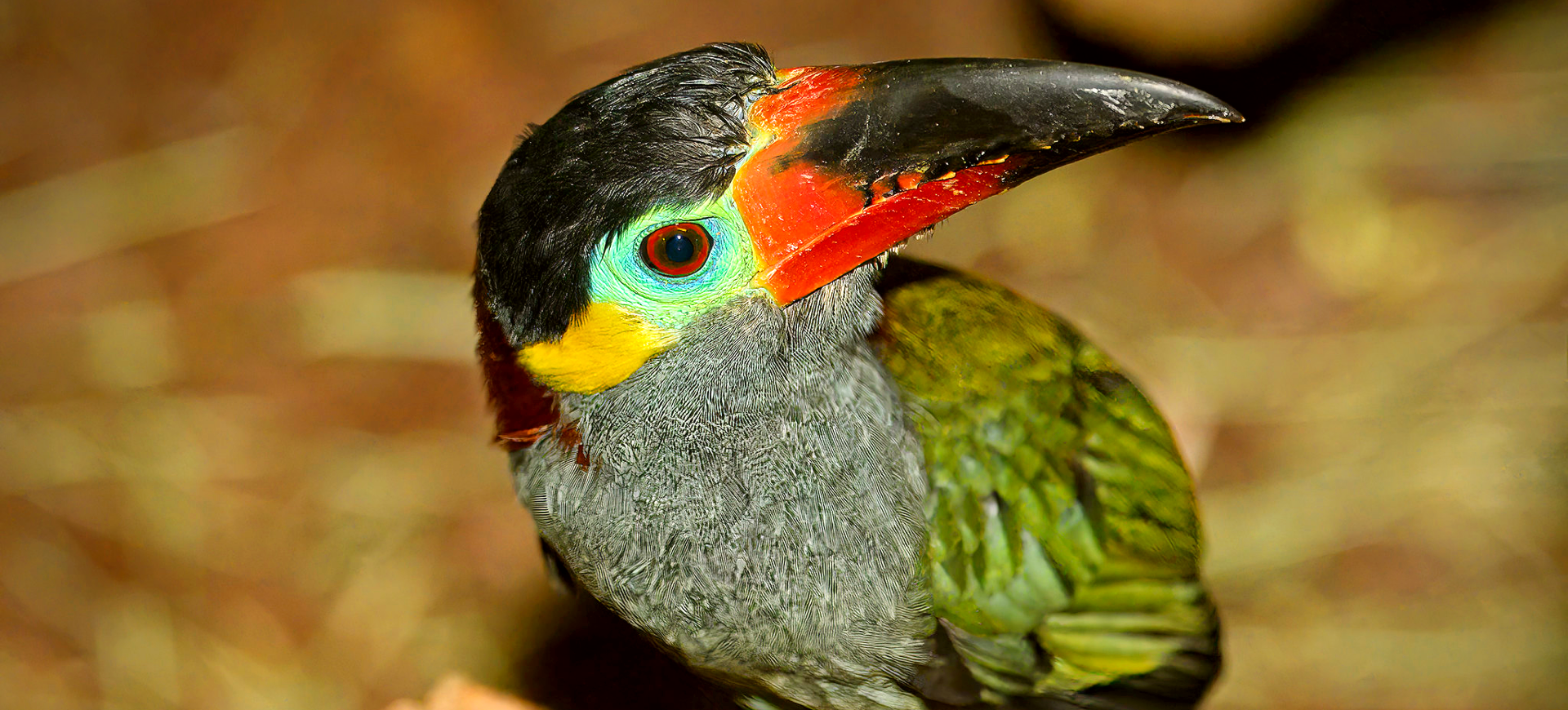
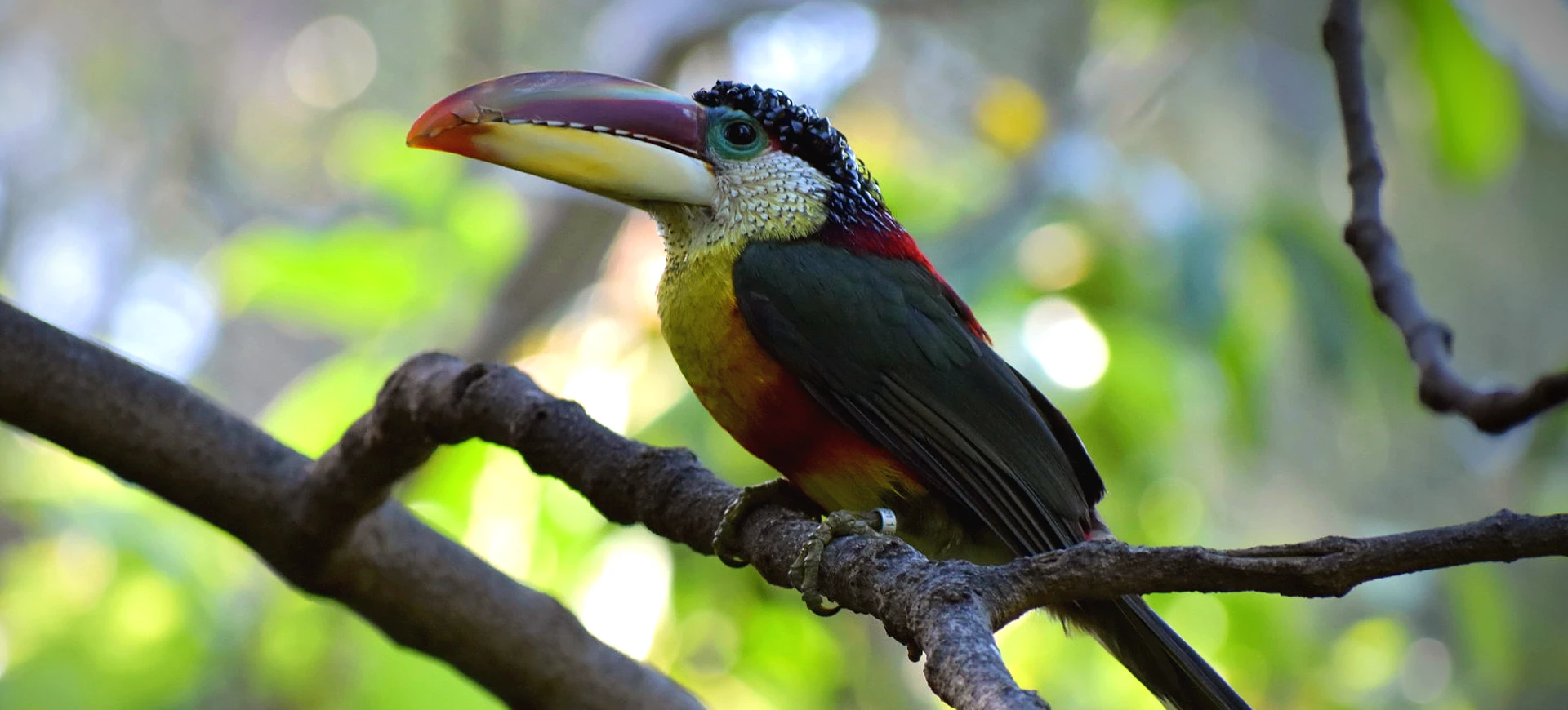
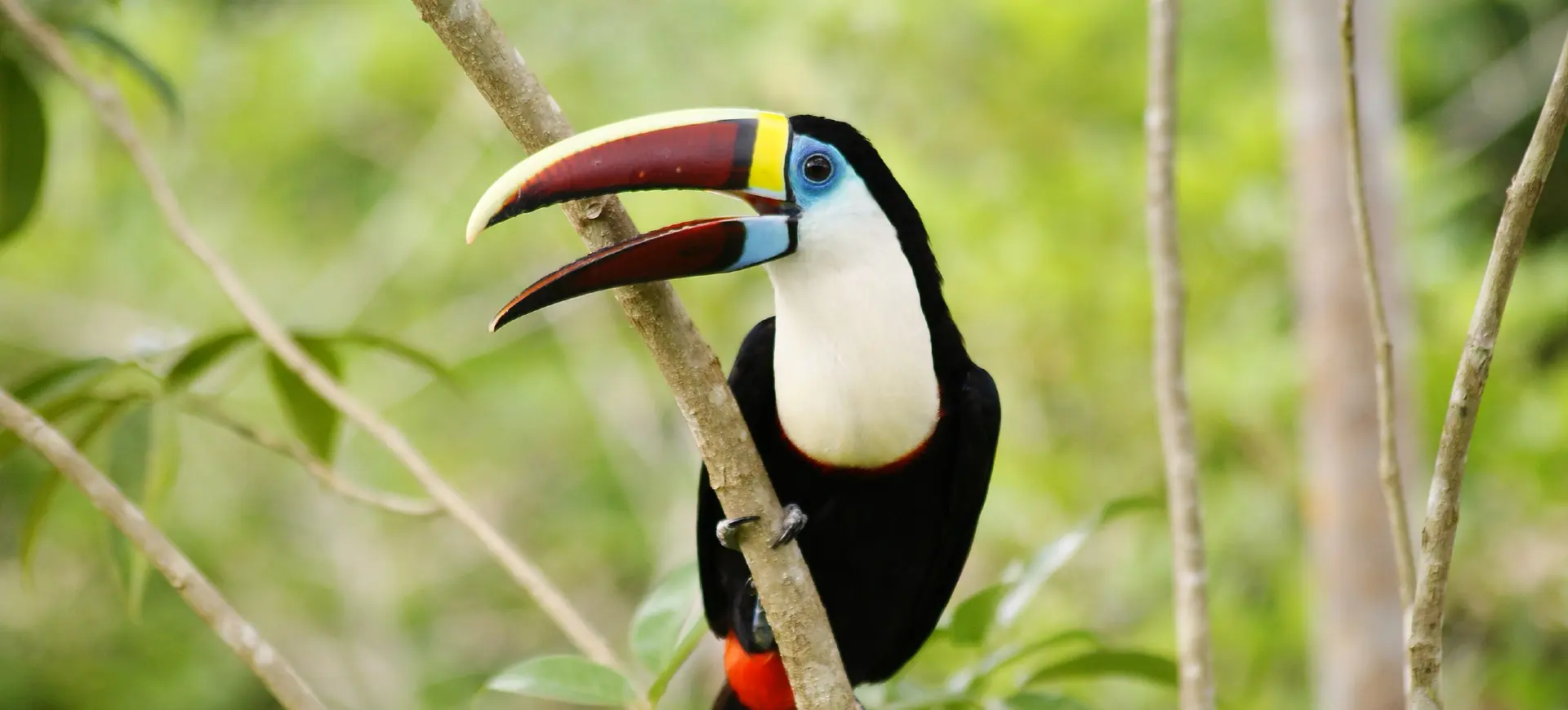
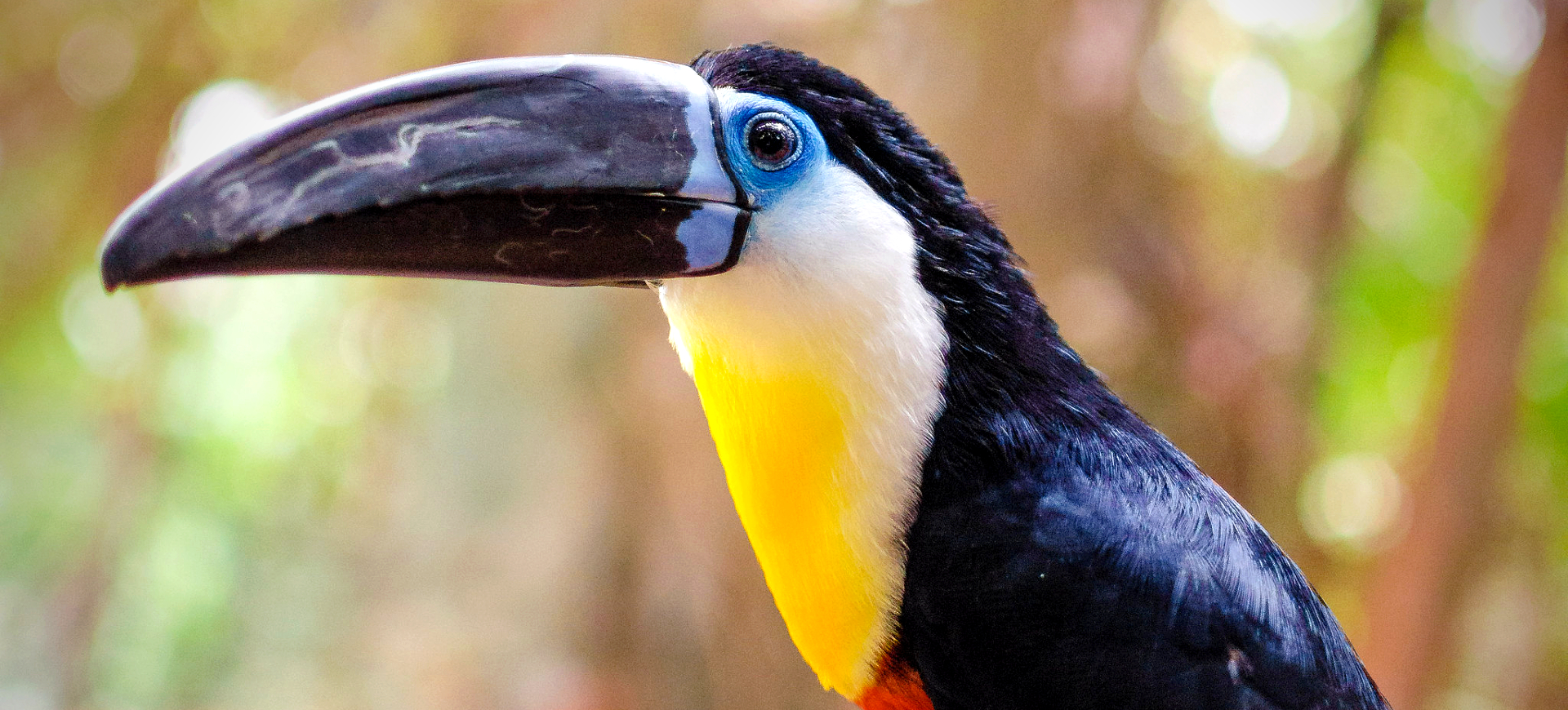
The Pale-mandibled Araçari, scientifically known as Pteroglossus erythropygius, is a vibrant and colorful member of the toucan family found in the western regions of Ecuador and the extreme southwestern part of Colombia. This bird is easily recognizable by its striking plumage and the distinctive pale mandible from which it derives its name. The black body has a bright red rump and a yellow collar around the neck, contrasting sharply against its creamy underparts and chestnut head.
The Pale-mandibled Araçari is an arboreal species that spends most of its life in the canopies of humid lowland and montane forests. It is a social species, often seen in small flocks that travel together in search of food. Their diet primarily consists of fruits, but they also eat insects and occasionally eggs or nestlings of other birds, which makes them important seed dispersers and participants in the control of insect populations. Their presence indicates a healthy forest ecosystem, making them vital to their native habitat’s biodiversity.
Despite its limited range, the Pale-mandible Araçari adapts well to altered forest habitats but remains dependent on suitable nesting sites in old trees. The primary threats to its population include habitat destruction due to deforestation and the illegal pet trade, driven by its exotic appearance. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the preservation of this species, focusing on habitat protection and enforcing laws against illegal trading.
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Type
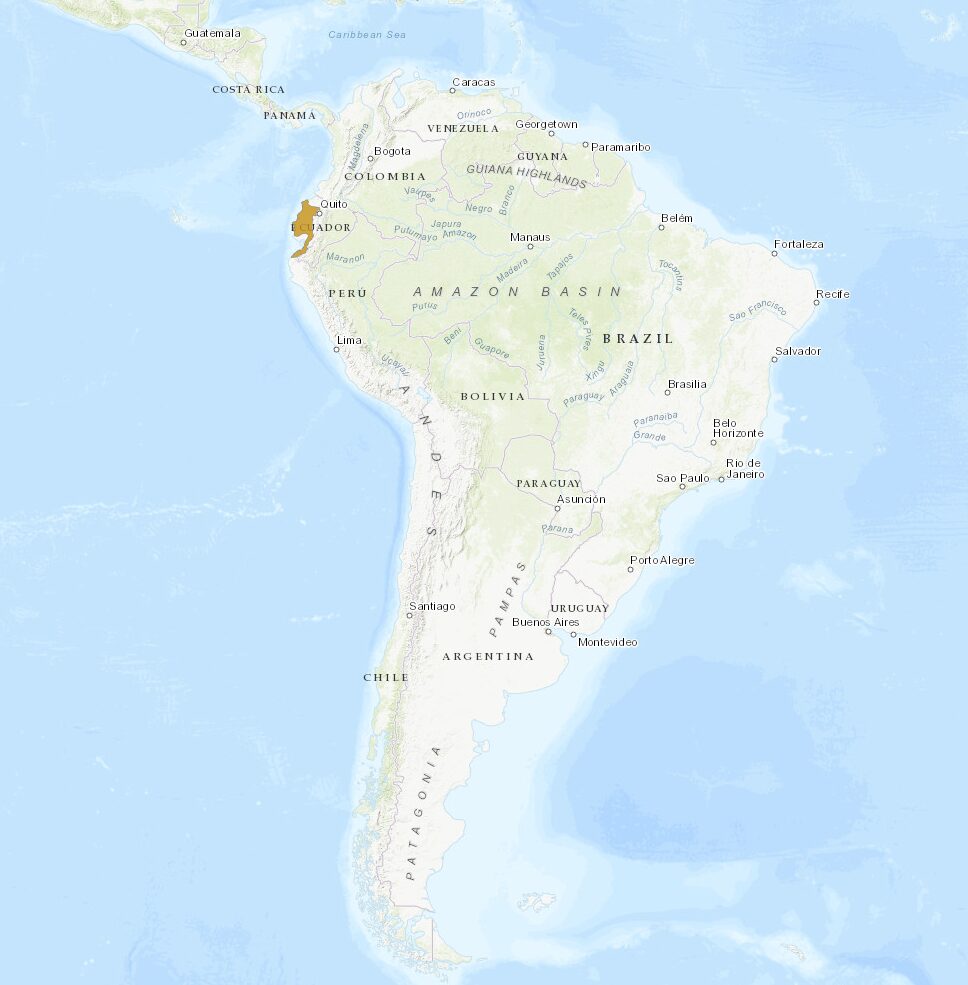
Current distribution:
The Pale-mandible Araçari is confined to a relatively small geographical range within the western Andean slopes of Ecuador and into the southwestern tip of Colombia. The species is locally common within this range in areas with extensive tracts of its native forest habitat. However, the bird's distribution is patchy and primarily restricted to regions that have not been overly fragmented by human activity.
Efforts are being made to map and protect critical areas of Araçari'smhabiAraçari'sital habiAraçari'sital for conservation. Maintaining connectivity between forest patches is also crucial to ensuring populations' genetic diversity and resilience.
Physical Description:
The Pale-mandible Araçari is a medium-sized bird, typically about 16 inches long, with a striking appearance characterized by its vibrant colors and patterns. Its most notable feature is the pale ivory bill, which stands out against its dark and richly colored plumage. The bird’s upperparts are predominantly black with a bright red rump and a distinct yellow collar separating its black throat from its chestnut head.
This species has relatively short wings and a long tail, which are adaptations to its life in dense forests where agility and maneuverability are more crucial than speed. The Pale-mandible Araçari’s zygodactyl feet, with two toes facing forward and two backward, allow it to cling to branches while feeding. The overall body structure of this bird, combined with its strong bill, is perfectly adapted for a diet that primarily consists of fruit but also includes insects and small vertebrates.

Lifespan: Wild: ~15 Years || Captivity: ~20 Years

Weight: Male: 6.2-8.8 oz (176-249 g) || Female: 5-6.5 oz (140-184 g)

Length: Male & Female: 16-17 inches (40-43 cm)
Characteristic:
Native Habitat:
The native habitat of the Pale-mandible Araçari includes the tropical and subtropical moist lowland and montane forests of western Ecuador and southwestern Colombia. These regions are characterized by high biodiversity and complex forest structures that provide abundant food and nesting opportunities for this species. The Pale-mandible Araçari is particularly dependent on the presence of old-growth trees for nesting, which makes it vulnerable to deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
Preserving these habitats is essential for the survival of the Pale-mandible Araçari and the countless other species that share this ecosystem. Conservation efforts must focus on protecting these forests from further degradation and promoting sustainable land use practices that accommodate human needs and wildlife conservation.
Climate Zones:
Biomes:
WWF Biomes:
Biogeographical Realms:
Continents:
Diet:
Diet & Feeding Habits:
The Pale-mandible AAraçari’sdiet is largely frugivorous, consisting predominantly of a wide variety of tropical fruits, which it plucks from the trees with its long, curved bill. This diet is supplemented by insects and occasionally by eggs, nestlings, or small vertebrates, making it an opportunistic feeder. The bbird’srole in its ecosystem extends to both seed dispersal and pest control, which helps maintain the ecological balance of its forest environment.
Regarding feeding behavior, Pale-mandible Araçaris often feed as a group, sharing large fruit sources. They also participate in mutualistic relationships with certain tree species, where the trees depend on the araçaris for seed dispersal. The bird’s ability to access different layers of the forest canopy allows them to exploit food resources that might be inaccessible to other species, highlighting their importance in the food web.
Mating Behavior:
Mating Description:
The Pale-mandible Araçari is known for its complex social structure and breeding behaviors, which include monogamous pair bonds that often last for several breeding seasons. During the mating season, males and females participate in nest-building, usually in cavities within dead trees. These cavities are also used for roosting outside the breeding season, protecting from predators.
The female typically lays two to four eggs per clutch, and both parents share the responsibilities of incubation and feeding the chicks. Their cooperative breeding behavior ensures a higher survival rate for the offspring, which is crucial given the challenges posed by their limited habitat.
Reproduction Season:
Birth Type:
Pregnancy Duration:
Female Name:
Male Name:
Baby Name:
Social Structure Description:
Pale-mandible Araçaris are social birds, often found in small groups of up to six individuals. These groups participate in cooperative feeding and breeding activities, which help individuals secure more food and reduce predation risk. The social structure of the Pale-mandible Araçari allows for complex interactions and communication among individuals, facilitating the sharing of resources and information about food and threats.
Understanding the social behavior of Pale-mandible Araçaris is important for developing effective conservation strategies, as social cohesion can impact the birds’ ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions and recover from population declines.
Groups:
Conservation Status:
Population Trend:
The population of the Pale-mandible Araçari is decreasing due to ongoing habitat loss and fragmentation. While precise population numbers are unknown, the species is reported to be locally common in suitable habitats within its range. However, the lack of comprehensive data on population trends and numbers highlights the need for further research and monitoring to assess the full impact of environmental changes on this species.
Conservation strategies focused on habitat preservation and the restoration of degraded forest areas are essential for stabilizing and potentially increasing the population of the Pale-mandible Araçari. Public awareness and involvement in conservation efforts are also crucial to mitigate the threats to this species.
Population Threats:
The primary threat to the Pale-mandible Araçari is habitat loss due to agricultural expansion, logging, and human settlement, which fragments its forest environment. The illegal pet trade also poses a risk due to the bird’s appealing appearance and exotic nature. Climate change threatens to alter the ecosystems where this bird thrives, potentially impacting food availability and breeding conditions.
Effective management of these threats requires integrated conservation measures, including legal protection of forests, sustainable land management practices, and enforcement against wildlife trafficking.
Conservation Efforts:
Conservation efforts for the Pale-mandibled Araçari include legal protection of its habitat, particularly in Ecuador and Colombia, where several protected areas have been established. Efforts to restore degraded forest areas and reconnect fragmented habitats are also underway to create a more resilient environment for this and other forest-dependent species.
Community engagement and environmental education programs are critical to increasing local support for conservation initiatives. These programs help local communities understand the ecological and economic benefits of preserving native forests, which is key to the long-term success of conservation efforts.
Additional Resources:
Fun Facts
- The Pale-mandible Araçari’s vibrant bill is not just for show; it helps the bird peel fruit, access pulp, intimidate rivals, and attract mates.
- Despite their colorful appearance, these birds can be quite difficult to spot in their forest habitats’ lush, green canopies.
- They are known for their playful behavior, often seen interacting with members of their group in a lively manner.
- Araçaris use their long, agile tongues to access nectar from flowers, making them important pollinators for some plant species.
- Their nesting strategy of using existing tree cavities helps protect their eggs and young from predators.
- Conservation efforts for the Pale-mandibled Araçari also benefit many other species within the rich biodiversity of the Andean forests.
- They have a wide vocal range, communicating over the dense forest noise.
- The Pale-mandible Araçari is part of the toucan family, known for its members’ striking bills and colorful appearance.
- This species’ dependency on old-growth forests for nesting highlights the importance of protecting mature forest ecosystems.
- Their social nature makes them a favorite among birdwatchers, who often observe their interactions in small, dynamic groups.