Overview
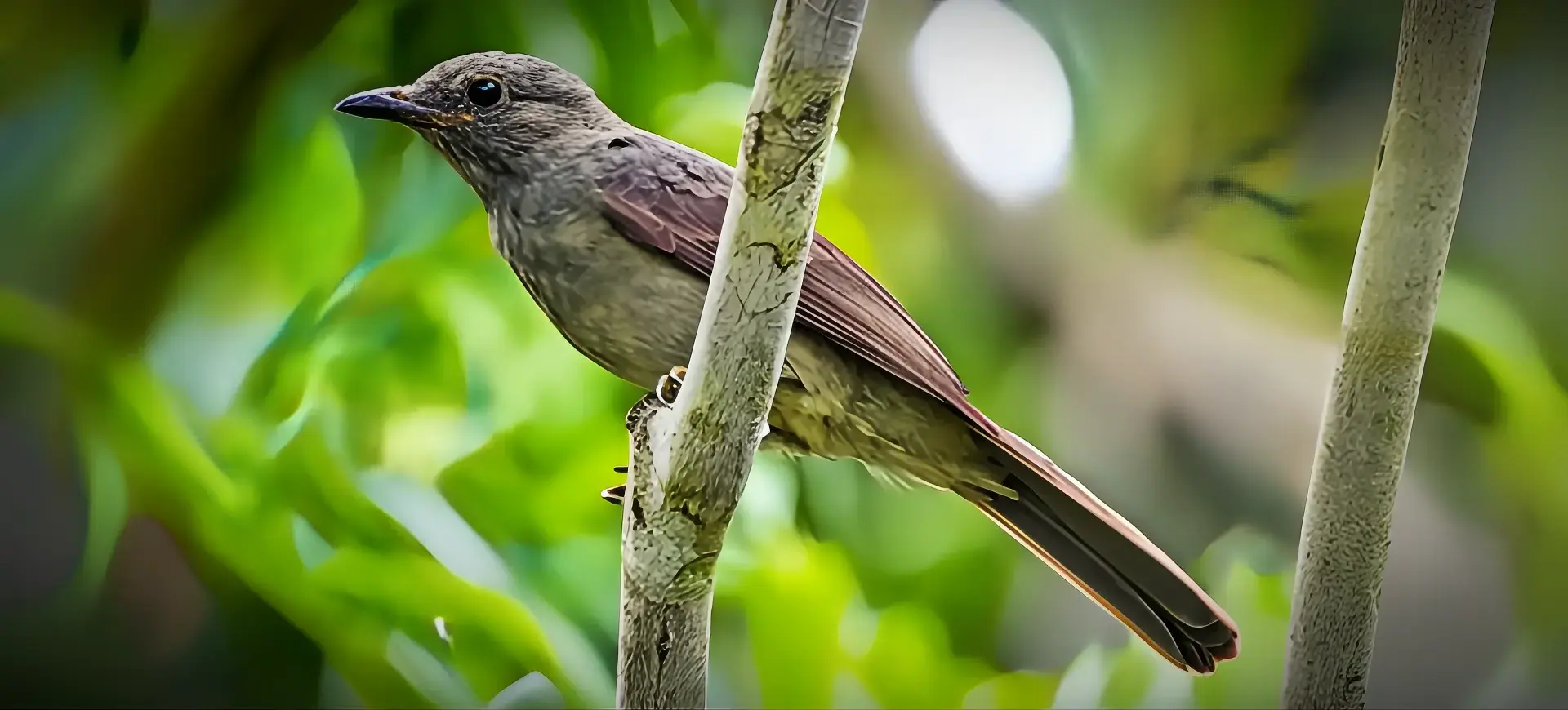
The Purple-throated Fruitcrow, scientifically known as Querula purpurata, is a distinctive bird species found in the neotropical forests of Central and South America. It is notable for its glossy black plumage, with males displaying a striking purple throat that becomes visible during vocalizations and displays. At the same time, females and juveniles have a less pronounced coloring. These medium-sized birds have a robust body and a broad bill and are adapted for their frugivorous diet. They inhabit the dense canopies of lowland rainforests, where they are often more easily heard than seen, thanks to their loud and raspy calls.
Social and gregarious, Purple-throated Fruitcrows form small groups or larger communities, engaging in cooperative breeding behaviors that are relatively uncommon among passerine birds. Their diet primarily consists of fruits, which they pluck from the foliage or catch in flight, and occasionally they supplement their diet with insects. The species plays a crucial role in their ecosystem as seed dispersers, contributing to the health and regeneration of their forest habitats. Despite their somewhat elusive nature, they are a key species for ornithologists and ecotourists drawn to their unique vocalizations and social structures.
Breeding season for the Purple-throated Fruitcrow involves complex social interactions and communal care for the young, a rarity among birds. The nests are simple platforms made of twigs located in the dense canopy, where group members collectively protect the eggs and feed the chicks. This cooperative breeding system strengthens social bonds within the group and enhances the survival rates of offspring, underscoring the interconnectedness of these birds with the vibrant ecosystems they inhabit.
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Type
Current distribution:
The Purple-throated Fruitcrow is distributed across a wide range in the neotropics, from Costa Rica and Panama through Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and into the Amazon basin of Brazil, extending to parts of Bolivia. This extensive distribution reflects their adaptability to forested environments within the neotropical region. Despite the broad range, their presence is often localized to areas with undisturbed forest cover, where they can find suitable nesting and foraging opportunities.
Their populations are generally stable in areas where their habitat is preserved, but they are susceptible to the effects of deforestation and habitat fragmentation. Conservation efforts focused on protecting large areas of contiguous forest are essential for maintaining healthy populations of Purple-throated Fruitcrows and other species that share their habitat. Their role in the ecosystem as seed dispersers makes them integral to the health and regeneration of tropical forests, emphasizing the need for ongoing conservation initiatives.
Physical Description:
The Purple-throated Fruitcrow is characterized by its predominantly glossy black plumage, which contrasts sharply with the purple throat patch found in males. This feature is especially prominent during the breeding season. They have a strong, stout build with a relatively short tail and broad wings suited to their life in the dense forest canopy. Both sexes are similar in appearance, but the female’s throat patch is less vibrant, and juveniles lack the purple coloring altogether. Their expressive eyes and broad bill, which are adept at handling a variety of fruits, add to their distinctive appearance.
In flight, the Purple-throated Fruitcrow’s powerful wingbeats are notable, allowing for quick maneuvers through the dense foliage of their rainforest home. They are medium-sized birds with a balanced proportion that aids their agility and elegance, whether foraging for fruits or interacting within their social groups. The deep, glossy sheen of their feathers reflects the sunlight in the canopy, making them a mesmerizing sight on the rare occasions they are visible against the backdrop of green foliage. Their vocalizations, a key aspect of their presence in the rainforest, are as distinctive as their appearance, echoing through the forest and signaling their location to others.

Lifespan: Wild: ~12 Years || Captivity: ~15 Years

Weight: Male: 3.5-4.1 oz (100-115 g) || Female: 3.3-3.9 oz (95-110 g)

Length: Male: 8.7-9.4 in (22-24 cm) || Female: 8.5-9.2 in (21.5-23.5 cm)

Top Speed: 20 mph (32 km/h)
Characteristic:
Native Habitat:
Purple-throated Fruitcrows are native to the neotropical rainforests of Central and South America, where they inhabit the dense, humid canopy of lowland forests. Their preferred habitat includes primary rainforests, secondary-growth forests, and occasionally wooded areas near water sources, showcasing their adaptability to various forest environments. These birds thrive in the biodiversity-rich ecosystems of the Amazon basin, extending their range from southern Central America through Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Brazil to Bolivia.
The complexity of the rainforest canopy offers the perfect habitat for the Purple-throated Fruitcrow, providing ample food sources and nesting sites. Preserving these habitats is crucial for the species’ survival, as deforestation and habitat degradation pose significant threats to their populations. Their reliance on dense forest environments highlights the importance of sustainable land-use practices and conservation efforts to protect these critical ecosystems.
Climate Zones:
Biomes:
WWF Biomes:
Biogeographical Realms:
Continents:
Diet:
Diet & Feeding Habits:
The Purple-throated Fruitcrow’s diet is predominantly frugivorous, consisting mainly of a wide variety of tropical fruits, which they skillfully pluck from the trees or occasionally catch in mid-air. This diet makes them vital for their ecosystem, as they act as seed dispersers, contributing significantly to the regeneration of their rainforest habitats. They have also been observed eating insects, particularly during the breeding season, which provides additional protein necessary for the development of their young.
These birds typically forage in the canopy, where their black plumage blends with the shadows of the foliage, making them difficult to spot despite their relatively large size. They are known to forage in groups, taking advantage of the abundance of fruit in their tropical rainforest environment. The feeding habits of the Purple-throated Fruitcrow highlight the bird’s adaptation to its environment, showcasing the interconnectedness of species within tropical ecosystems. Their role as seed dispersers underscores the importance of their conservation for maintaining biodiversity in their native habitats.
Mating Behavior:
Mating Description:
The Purple-throated Fruitcrow participates in a cooperative breeding system, a unique aspect of their social behavior. In this system, several individuals within a group contribute to caring for the young, including feeding and protecting the offspring. This communal approach to rearing young allows for a higher survival rate of chicks, as parenting duties are shared among multiple adults, reducing the burden on any single pair of birds.
Nesting occurs in the dense canopy, where simple platforms hold the eggs. The nests are relatively exposed, making cooperative defense against potential predators vital for the young’s survival. During the breeding season, the males’ vibrant purple throat becomes more pronounced as a visual signal to females and rivals. The intricate social dynamics of their breeding system, including mate selection and group hierarchy, play a crucial role in their populations’ reproductive success and overall stability.
Reproduction Season:
Birth Type:
Pregnancy Duration:
Female Name:
Male Name:
Baby Name:
Social Structure Description:
The social structure of the Purple-throated Fruitcrow is characterized by cooperative breeding behavior and the formation of small—to medium-sized groups. These groups consist of breeding pairs, offspring, and sometimes unrelated adults, all of whom participate in the care of the young. This structure enhances the chances of offspring survival and distributes the workload among group members, showcasing a high degree of social cooperation and communication.
Within these groups, a complex hierarchy influences foraging, breeding, and nesting behavior. The strong social bonds formed within these communities are crucial for their survival, protecting against predators and ensuring efficient use of resources. The cooperative nature of the Purple-throated Fruitcrow’s social structure is a fascinating aspect of their behavior, reflecting the adaptability and complexity of avian social systems.
Groups:
Conservation Status:
Population Trend:
The population of the Purple-throated Fruitcrow is considered stable across its broad range, primarily due to its adaptability to various forest environments and the extensive, though fragmented, habitats available in the neotropics. These birds are relatively common in areas of undisturbed forest, where they form vital ecosystem components. However, their dependence on dense canopy cover makes them vulnerable to deforestation and habitat fragmentation, which could threaten localized populations.
Efforts to monitor the species are ongoing, with conservationists emphasizing the importance of preserving large tracts of rainforest to ensure the continued stability of their populations. The Purple-throated Fruitcrow’s role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration makes it a priority species for conservation, as its well-being directly impacts the health of tropical forest ecosystems. Protecting its habitat not only benefits the Purple-throated Fruitcrow but also supports the vast biodiversity found within neotropical rainforests.
Population Threats:
The primary threat facing the Purple-throated Fruitcrow is habitat loss due to deforestation and the degradation of tropical rainforests. Expanding agriculture, logging, and urban development into forested areas reduces the availability of suitable habitats for nesting and foraging, impacting their ability to sustain healthy populations. Additionally, climate change poses an indirect threat by altering the ecosystems they depend on, potentially affecting the distribution and abundance of fruit trees that form the basis of their diet.
Habitat fragmentation is another significant concern, as it isolates populations and disrupts the genetic flow between groups, potentially leading to decreased genetic diversity and increased vulnerability to environmental changes. Conservation efforts must address these threats by promoting sustainable land use practices and protecting large areas of contiguous forest to ensure the survival of the Purple-throated Fruitcrow and the rich biodiversity of the neotropical rainforests.
Conservation Efforts:
Conservation initiatives for the Purple-throated Fruitcrow focus on habitat preservation and protecting the tropical rainforests they inhabit. Establishing protected areas and national parks, where logging and agricultural expansion are restricted, is crucial for safeguarding their habitats. Conservation organizations and governments are working together to implement sustainable land-use practices that balance human populations’ needs with preserving biodiversity.
Reforestation and habitat restoration projects also play an important role in conservation efforts, helping to reconnect fragmented habitats and increase the available territory for the Purple-throated Fruitcrow and other forest-dwelling species. Education and community involvement are key components of these initiatives, raising awareness about the importance of tropical rainforests and the species they support. By promoting coexistence and understanding, conservation efforts aim to ensure the long-term survival of the Purple-throated Fruitcrow and the intricate ecosystems they call home.
Additional Resources:
Fun Facts
- The Purple-throated Fruitcrow is one of the few passerine birds engaged in cooperative breeding.
- Their glossy black plumage and striking purple throat make them one of the more visually distinctive species in their habitat.
- Despite their name, only the males have a prominently purple throat, most visible during vocalizations and displays.
- They play a critical role in their ecosystem as seed dispersers, aiding in the regeneration of tropical forests.
- The species’ loud and raspy calls echo through the rainforest, serving as a communication tool within their groups.
- They are adept at catching fruits mid-air, showcasing their agility and precision.
- The Purple-throated Fruitcrow’s habitat spans several countries, reflecting their adaptability to different forest environments.
- Their diet consists almost entirely of fruits, but they occasionally eat insects, especially when feeding chicks.
- The construction of their nests is a communal effort, with several birds contributing to the building and protection of the nest site.
- Conservation efforts for the Purple-throated Fruitcrow emphasize the importance of protecting large tracts of undisturbed rainforest.