Overview
The Blue-and-yellow Macaw, also known as the Blue-and-gold Macaw, is a large South American parrot characterized by its vibrant colors. Its body is adorned with striking royal blue on the upper parts and golden yellow on the underparts, often mixed with shades of green. Its robust beak is solid black, and the area around the eyes exhibits featherless white skin. This bird is stunning and known for its high intelligence and remarkable talking abilities.
The macaw’s overall length is approximately 34-36 inches, with their long, streamlined tails making up over half of this length. Both sexes have similar appearances, although males are generally larger. The blue-and-yellow macaw’s playful personality, social nature, and impressive mimicking ability make them popular among bird enthusiasts and zoo visitors. Like many parrots, they possess a boisterous nature and are highly vocal, emitting loud squawks and screams.
Blue-and-yellow Macaws are often seen in large flocks and are very social in the wild. Their diet primarily consists of fruits, seeds, and nuts. These birds are monogamous and mate for life, often seen flying together in pairs within the larger flock. They display remarkable longevity, with over 60 years in some cases.
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Type
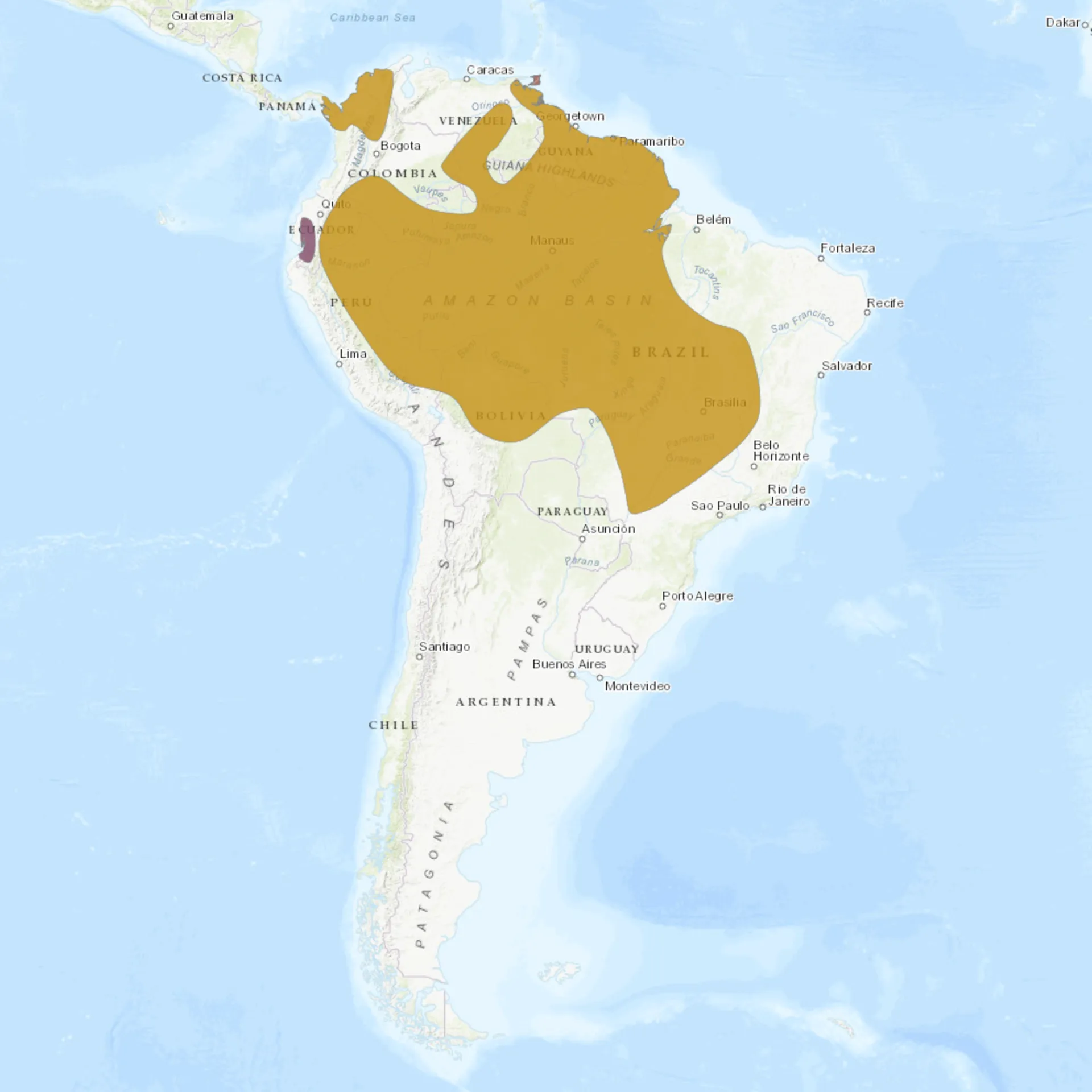
Current distribution:
Despite their wide distribution range, the populations of Blue-and-yellow Macaws have been declining due to habitat loss and illegal pet trade. They are still found across a broad swathe of Central and South America, from Panama in Central America south into Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, and Peru.
Significant populations exist in the Amazon Rainforest, where these macaws exploit abundant fruit and nut resources. There are also reported populations in savannas, woodlands, and scrub forests near water bodies like rivers or swamps. However, the exact numbers in the wild are difficult to ascertain due to their broad and often inaccessible habitats.
Physical Description:
The Blue-and-yellow Macaw is a large parrot, measuring approximately 34 to 36 inches in total length. They are strikingly beautiful, with vibrant royal blue and golden yellow hues adorning their bodies. The upper parts of their bodies are predominantly royal blue, including their wings and tail, while the underparts are golden yellow with hints of green. Their head is a slightly lighter blue, with a characteristic bare white patch of skin around their eyes. Their black, strong, curved beak contrasts with their bright feathers, perfectly adapted to crack open hard nuts and seeds.
Blue-and-yellow Macaws display sexual monomorphism, meaning that males and females look virtually identical. The main difference lies in the size, with males generally slightly larger than females. However, this difference is usually subtle and can’t always be discerned with the naked eye. Their eyes start as grey or brown in juveniles and turn to a striking yellow-gold as they mature.

Lifespan: Wild: ~35 Years || Captivity: ~60 Years

Weight: Male: 2-3 lbs (0.9-1.4 kg) || Female: 2-2.6 lbs (0.9-1.2 kg)

Length: Male: 34-36 in (86-91 cm) || Female: 32-34 in (81-86 cm)

Wingspan: Male & Female: 41-45 in (104-114 cm)

Top Speed: 35 mph (56 km/h)
Characteristic:
Native Habitat:
Blue-and-yellow Macaws are native to the subtropical and tropical regions of Central and South America. They inhabit a wide range of environments, from the rainforests of the Amazon basin to open woodlands and savannah-like landscapes. These macaws favor areas near rivers and water bodies, which provide a steady supply of their favorite foods, such as palm fruits.
These parrots are strong flyers, spending much of their time high in the canopy, which offers protection from predators and access to food. They also roost in the tree branches and nest in tree cavities. During the day, they fly long distances for food, returning to their roosting sites at dusk.
Climate Zones:
Biomes:
Biogeographical Realms:
Continents:
Diet:
Diet & Feeding Habits:
Blue-and-yellow Macaws are omnivores, predominantly frugivores. In the wild, their diet consists mainly of fruits, seeds, nuts, and berries. They are also known to consume leaves, flowers, and stems. They are particularly fond of palm fruits and are adept at breaking open even the toughest shells with their powerful beaks. Their large, strong beaks enable them to access food that other birds cannot, making them crucial for seed dispersion in their ecosystems.
While foraging, they typically use their feet to hold and manipulate food items, bringing them to their mouth. In captivity, their diet can be supplemented with high-quality pellet feed, fresh fruits, vegetables, and a moderate amount of nuts. Providing them with a varied diet is crucial, ensuring they receive all necessary nutrients. Access to clean, fresh water is a must for all birds.
Mating Behavior:
Mating Description:
Blue-and-yellow Macaws are monogamous and form lifelong pair bonds. They exhibit elaborate courtship displays, including mutual preening, beak touching, and wing flapping. These displays not only strengthen their bonds but also serve to synchronize their reproductive readiness.
The breeding season varies according to the geographical location, usually aligning with the onset of the rainy season. They nest in tree cavities, often at great heights, which protects them from predators. After mating, the female lays 2-3 eggs, which she incubates for approximately 28 days. During this period, the male forages and feeds the female. After hatching, both parents are involved in caring for the chicks.
Reproduction Season:
Birth Type:
Pregnancy Duration:
Female Name:
Male Name:
Baby Name:
Social Structure Description:
Blue-and-yellow Macaws are highly social birds, often found in flocks that can number dozens to hundreds of birds. Within these flocks, mated pairs fly close together, their wings nearly touching. They communicate using various vocalizations, body language, and feather displays.
During the day, they forage and fly together, returning to their communal roosting sites at dusk. They exhibit cooperative behaviors, such as mutual preening and food sharing. They are known for their playful behavior and are often seen engaging in aerial acrobatics, games, and other forms of play.
Groups:
Conservation Status:
Population Trend:
The population of the Blue-and-yellow Macaw in the wild is challenging to quantify due to their expansive range and the inaccessibility of much of their habitats. While they are still found throughout their historical range, population numbers are declining. The primary reasons for this decline are habitat loss due to deforestation and the illegal pet trade.
These birds are prevalent in captivity due to their striking colors, playful personalities, and ability to mimic human speech. Zoos, aviculture enthusiasts, and bird breeders around the world maintain populations. They are often bred in captivity, contributing to a steady population outside their native range.
Population Threats:
The Blue-and-yellow Macaw faces several threats that have led to population declines. Habitat loss due to deforestation for agriculture, logging, and urbanization is a significant threat, leading to the fragmentation and loss of their habitats. They are hunted for their feathers and meat in some parts of their range.
The illegal pet trade also poses a significant threat. Despite international laws and treaties designed to protect them, these birds are often captured and sold as pets due to their attractive colors and ability to mimic human speech. Capturing these birds often involves destructive methods that can harm or kill many individuals.
Conservation Efforts:
There are several ongoing conservation efforts to protect and conserve the Blue-and-yellow Macaw. Many of these efforts involve habitat protection and restoration and enforcing laws against hunting and the illegal pet trade. Conservation organizations are working to raise awareness about the threats these birds face, and some run captive breeding and reintroduction programs to bolster wild populations.
Additionally, local communities are increasingly involved in conservation efforts. Some programs provide alternative income sources to communities that might otherwise engage in parrot hunting or the pet trade. Ecotourism is one such income source, where the presence of macaws can attract tourists and generate income for the community.
Additional Resources:
Fun Facts
- Blue-and-yellow Macaws can live up to 60 years in captivity, one of the longest lifespans of any parrot species.
- They have an uncanny ability to mimic human speech and other sounds.
- Their powerful beaks can exert up to 2000 psi pressure, allowing them to crack open hard-shelled nuts and seeds.
- They are monogamous and mate for life.
- Macaws’ feet are zygodactyl, meaning they have two toes facing forward and two facing backward, which aids in gripping branches and handling food.
- The bare skin patch on their faces has a pattern of lines unique to each bird, similar to a human fingerprint.
- They exhibit “blushing” – the bare skin on their faces can change color with their mood.
- Macaws are known to eat clay from riverbanks, believed to neutralize toxins in some food sources.
- Despite their vibrant colors, these macaws can blend surprisingly well into the foliage, providing them with excellent camouflage.
- They communicate using a range of vocalizations, including squawks, screams, and even song-like calls.