Overview
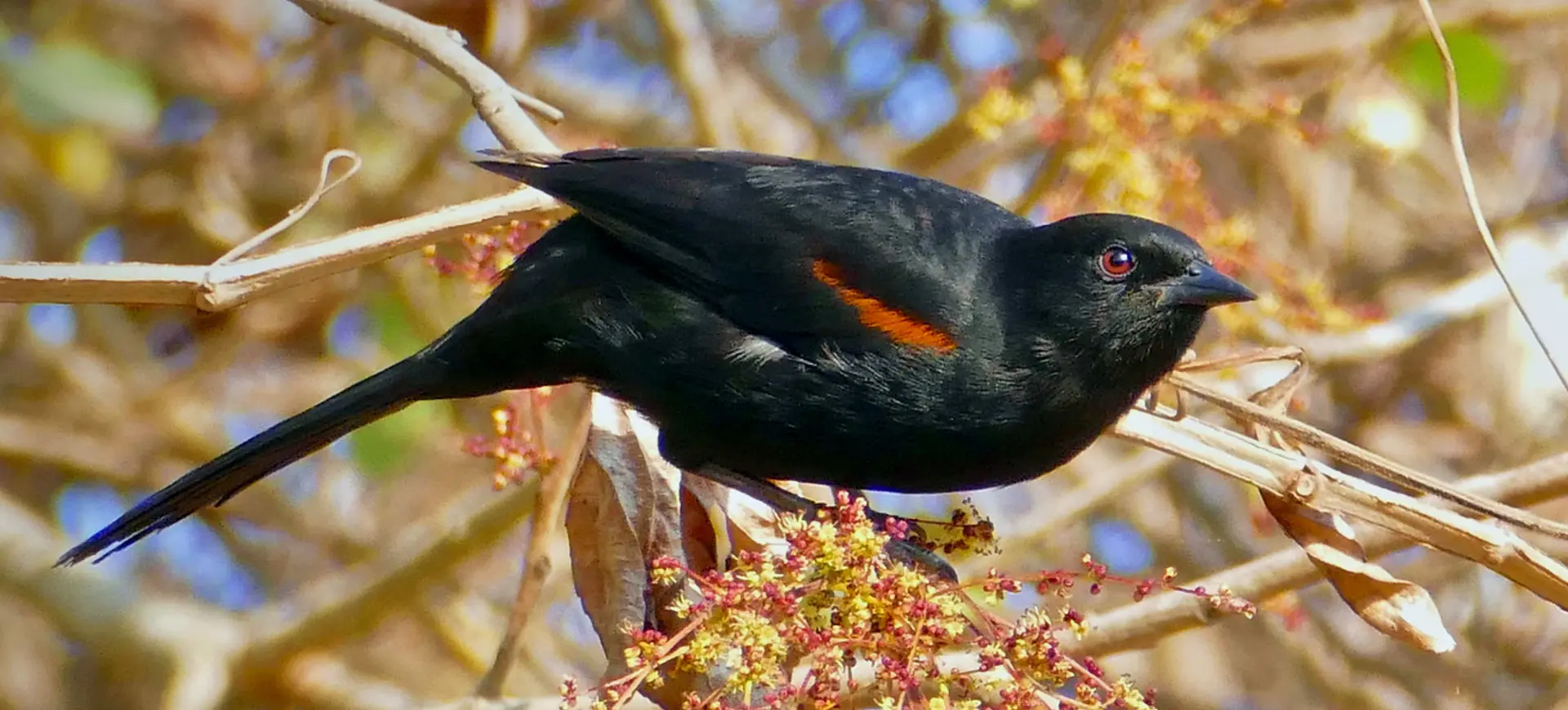
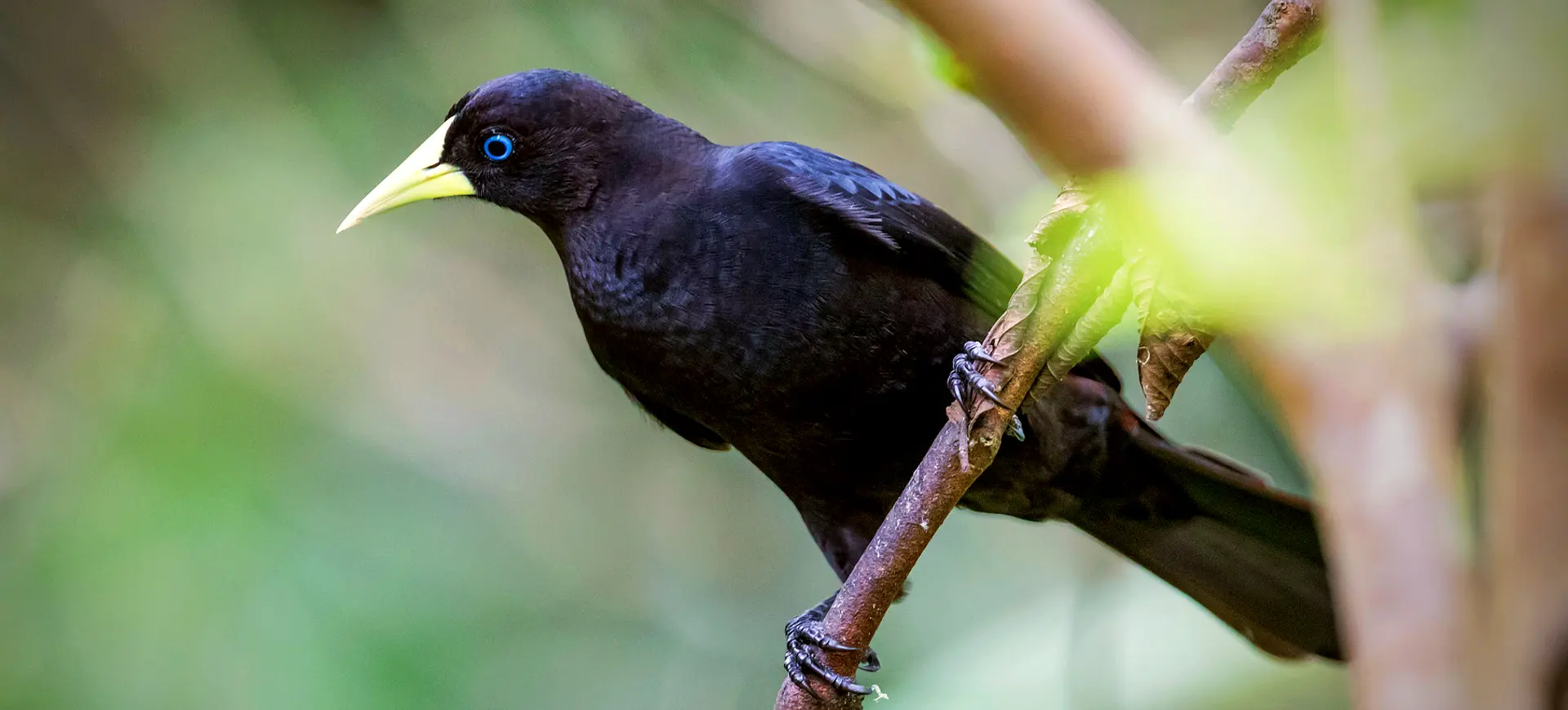
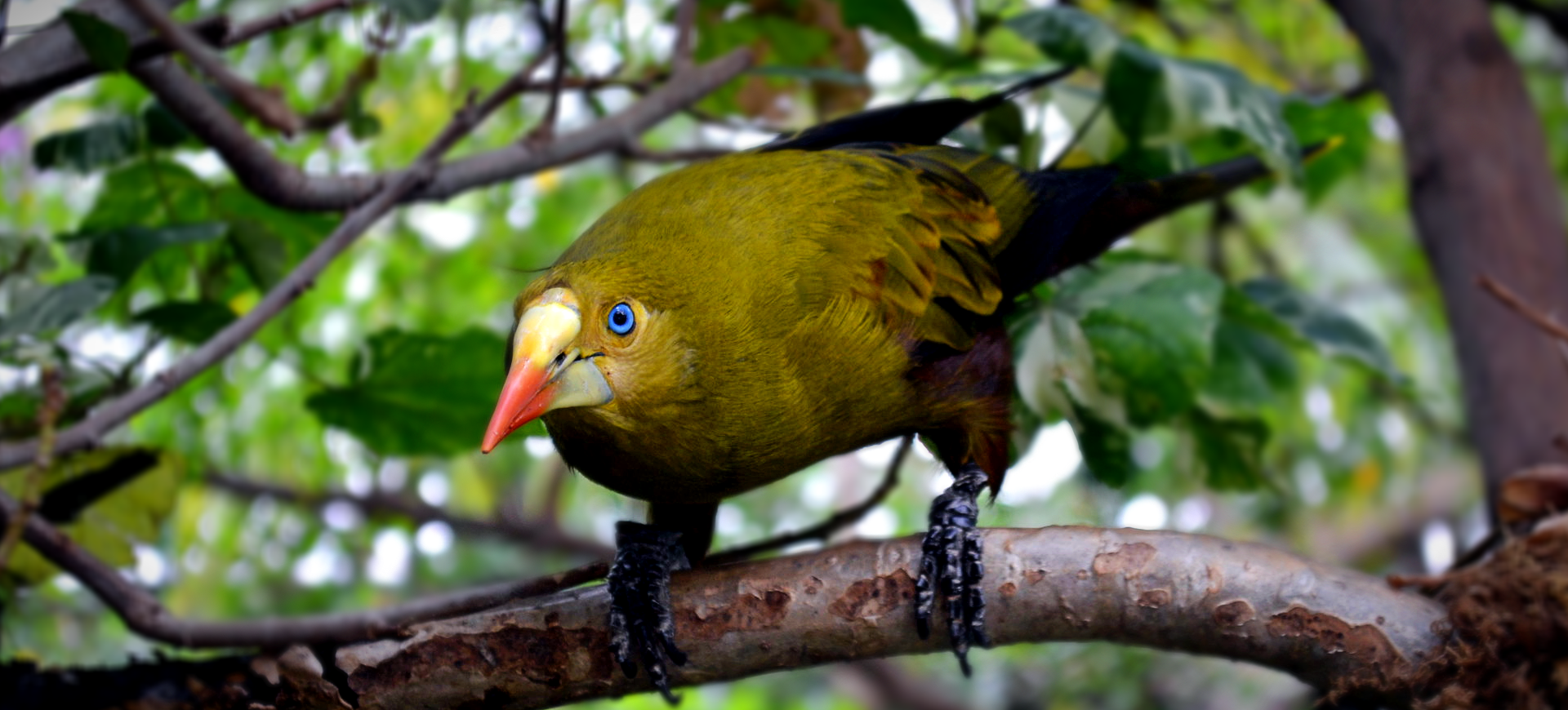
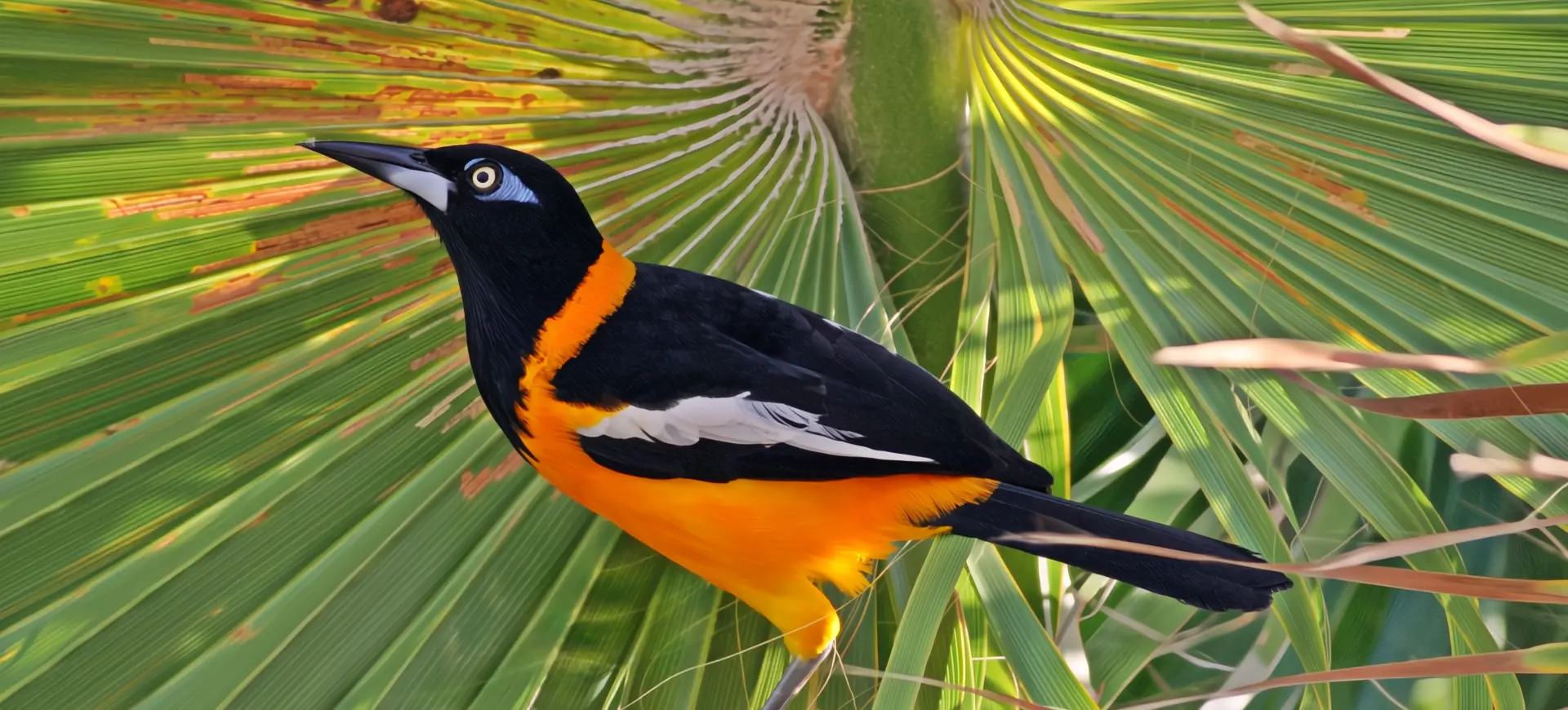
The Crested Oropendola, scientifically known as Psarocolius decumanus, is a fascinating bird species native to South America. Recognizable by its striking black plumage, vibrant yellow tail feathers, and unusual, pendulous nest, this bird is a member of the oropendola family, noted for its complex social structure and intriguing behaviors. Males are significantly larger than females and boast a distinctive crest of feathers on their heads, which is particularly prominent during courtship displays. The bird’s vocalizations are equally captivating, comprising a series of clicks, whistles, and gurgles that contribute to the auditory landscape of its habitat.
Crested Oropendolas inhabit tropical forests, savannas, and open woodlands, where they can be seen foraging for fruits, seeds, and insects. Their diet plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, thus aiding in maintaining their ecosystems. These birds are known for their remarkable nesting habits, constructing long, hanging nests from tree branches to protect their eggs and chicks from predators. The species’ social dynamics are complex, with colonies often comprising several dozen individuals, including a dominant male, several females, and their offspring.
Despite habitat destruction and fragmentation threats, the Crested Oropendola remains relatively abundant in areas where suitable habitats persist. Conservation efforts are focused on preserving the tropical forests and woodlands that are vital for the survival of this species, highlighting the importance of sustainable environmental practices to ensure the continued presence of the Crested Oropendola and the biodiversity of South American ecosystems.
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Sub Species
Type
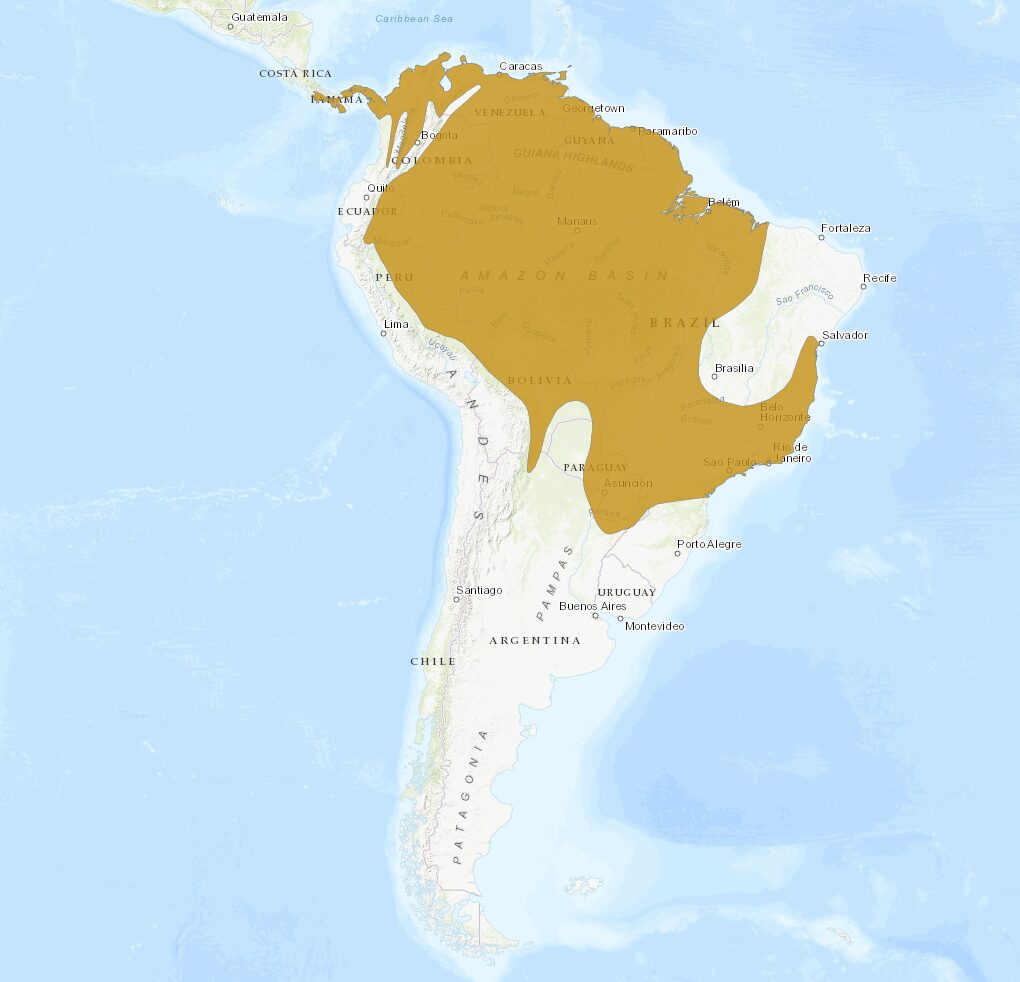
Current distribution:
Crested Oropendolas are distributed widely across South America, with their range extending from Panama through Colombia, Venezuela, and the Guianas down into Brazil, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. Despite this extensive range, the species faces challenges from habitat loss in some areas, which has led to localized population declines. Monitoring and protecting their habitats is crucial for ensuring the species' long-term viability.
The presence of Crested Oropendolas across diverse ecosystems highlights their adaptability and the importance of cross-border conservation initiatives. International cooperation is key to addressing these birds' environmental challenges, including deforestation, climate change, and the illegal pet trade. By prioritizing habitat conservation, we can help secure a stable future for the Crested Oropendola and the rich biodiversity of South America's tropical regions.
Physical Description:
The Crested Oropendola is an impressively sized bird. Males reach lengths of up to 50 cm, including their long, forked tails, which are striking yellow and contrast sharply against their mostly black bodies. The glossy black plumage exhibits a blue-green iridescence in sunlight, while the crest of feathers on the head is a defining characteristic of the species. Females are smaller and less vibrant than males but share the distinctive yellow tail feathers that make these birds so recognizable.
In addition to their visual allure, Crested Oropendolas possess a unique, wattle-like structure that dangles from the base of their beaks, adding to their exotic appearance. This feature is more pronounced in males and used in elaborate courtship rituals. Their eyes, encircled by patches of bare, blue skin, add to the striking contrast of their dark plumage, making them one of the more visually distinctive birds within their range.

Lifespan: Wild: ~15 Years || Captivity: ~20 Years

Weight: Male: 0.66-1.05 lbs (300-480 g) || Female: 0.4-0.6 lbs (180-280 g)

Length: Male: 16-19 in (41-50 cm) || Female: 14-16 in (36-41 cm)
Characteristic:
Native Habitat:
The Crested Oropendola inhabits a wide range of environments across South America, from the tropical rainforests of the Amazon basin to the open woodlands and savannas. They are particularly prevalent in areas with abundant tree cover, which provides essential resources for nesting and foraging. The adaptability of the Crested Oropendola to various habitats has been key to its survival, allowing it to thrive in regions with intact natural landscapes.
The conservation of these habitats is critical for maintaining the populations of Crested Oropendolas, as deforestation and habitat fragmentation pose ongoing threats to their existence. Protected areas and sustainable land management practices are essential for preserving the biodiversity of these environments, ensuring a future for the Crested Oropendola and countless other species that depend on these ecosystems.
Biomes:
Biogeographical Realms:
Continents:
Diet:
Diet & Feeding Habits:
Crested Oropendolas are omnivorous, eating a variety of fruits, seeds, nectar, and insects. Their feeding habits play a significant role in pollinating flowers and dispersing seeds, contributing to the health and diversity of their habitats. They often forage in groups, taking advantage of the abundance of food sources in their tropical forest environments.
These birds are adept at using their strong bills to extract seeds and nectar from fruits and flowers, showcasing their importance as agents of seed dispersal and pollination within their ecosystems. The variety in their diet reflects the biodiversity of their habitats, underscoring the need for conservation efforts to preserve these environments for the benefit of the Crested Oropendola and other wildlife.
Mating Behavior:
Mating Description:
Crested Oropendolas exhibit unique mating behaviors, with males performing elaborate displays to attract females. These displays include vocalizations, wing flapping, and swinging from branches, showcasing their vibrant plumage and physical prowess. The dominant male typically mates with multiple females who are responsible for building the nests and raising the young.
The nests of Crested Oropendolas are engineering marvels constructed as long, hanging structures woven from fibers and suspended from tree branches. This design protects from predators and the elements. The communal aspect of their nesting sites, where several nests are often found close together, highlights the complex social structure of these birds and the importance of group dynamics in their reproductive strategy.
Reproduction Season:
Birth Type:
Pregnancy Duration:
Female Name:
Male Name:
Baby Name:
Social Structure Description:
Crested Oropendolas are highly social birds. They form large colonies that include a dominant male, several females, and their offspring. The colony’s social hierarchy is evident in the distribution of nesting sites and access to food resources. These birds exhibit complex behaviors, including cooperative breeding and communal territory defense.
The intricate social dynamics of Crested Oropendolas play a critical role in their survival and reproductive success. Understanding these behaviors is essential for conservation efforts, as it provides insights into the species’ habitat requirements and the impacts of environmental changes on their populations.
Groups:
Conservation Status:
Population Trend:
The IUCN lists the Crested Oropendola as Least Concern, indicating a relatively stable population across its wide range. This status is attributed to the bird’s adaptability to habitats and presence in several protected areas. However, continuous monitoring is essential, as local populations could be affected by environmental changes and human activities.
Conservation initiatives focusing on habitat preservation and managing natural resources are vital for ensuring the continued prosperity of Crested Oropendola populations. Education and community engagement play significant roles in conservation efforts, fostering a greater appreciation for wildlife and the importance of ecological balance.
Population Threats:
The primary threats to the Crested Oropendola include habitat destruction due to logging, agriculture, and urban expansion, which result in the loss of nesting and foraging sites. Additionally, they are captured for the pet trade in some areas, further impacting their numbers. Climate change also poses a potential threat, altering their habitats and affecting food availability.
Mitigating these threats requires a multifaceted approach, including legal protection of forests, sustainable land-use practices, and efforts to curb the illegal wildlife trade. Conservation strategies must be adaptive and inclusive of local communities to ensure the effective protection of the Crested Oropendola and its habitat.
Conservation Efforts:
Conservation efforts for the Crested Oropendola involve habitat protection, restoration projects, and establishing protected areas. Initiatives aimed at sustainable agriculture and forestry practices help reduce habitat destruction and fragmentation. Education programs and community-based conservation projects encourage local involvement in protecting these birds and their ecosystems.
International cooperation and research are crucial for understanding the ecological needs of the Crested Oropendola and developing effective conservation strategies. By prioritizing habitat conservation and engaging local communities in preservation efforts, we can ensure a stable future for the Crested Oropendola and the diverse ecosystems they inhabit.
Additional Resources:
Fun Facts
- The Crested Oropendola’s nests resemble large hanging baskets and can be over 1 meter long and meticulously woven from fibrous materials.
- These birds have a unique vocal repertoire, including melodious whistles and mechanical clicks, contributing to the auditory landscape of their habitats.
- Indigenous peoples often use the bright yellow tail feathers of the Crested Oropendola in ceremonial attire and handicrafts, valuing their vibrant color and beauty.
- Despite their large size and elaborate nests, Crested Oropendolas are agile flyers, adept at maneuvering through dense forest canopies.
- Crested Oropendolas play a crucial ecological role as pollinators and seed dispersers, facilitating the growth and spread of numerous plant species within their environment.
- The social structure within Crested Oropendola colonies is complex, featuring a clear hierarchy that influences nesting site distribution and access to resources.
- These birds are known to form large colonies, with a dominant male overseeing several females and their offspring, showcasing their advanced social organization.
- The male Crested Oropendola’s dramatic courtship display involves bowing, spreading his tail, and swinging on branches to attract females.
- Crested Oropendolas have a wattle-like structure that dangles from the base of their beak, are more pronounced in males, and are used in elaborate courtship rituals.
- Conservation efforts to protect the Crested Oropendola also benefit many other species that share their tropical forest homes, highlighting their importance in maintaining biodiversity.