Overview
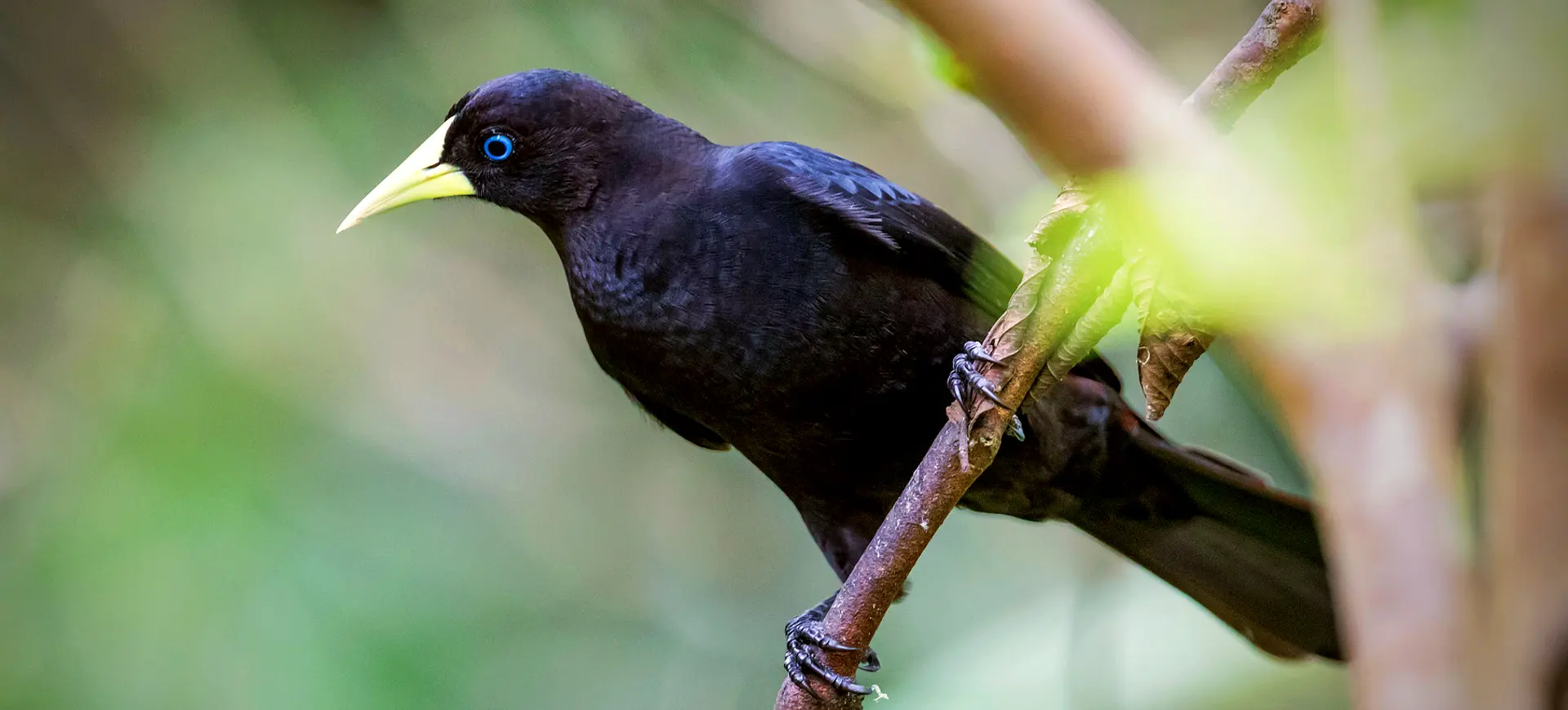
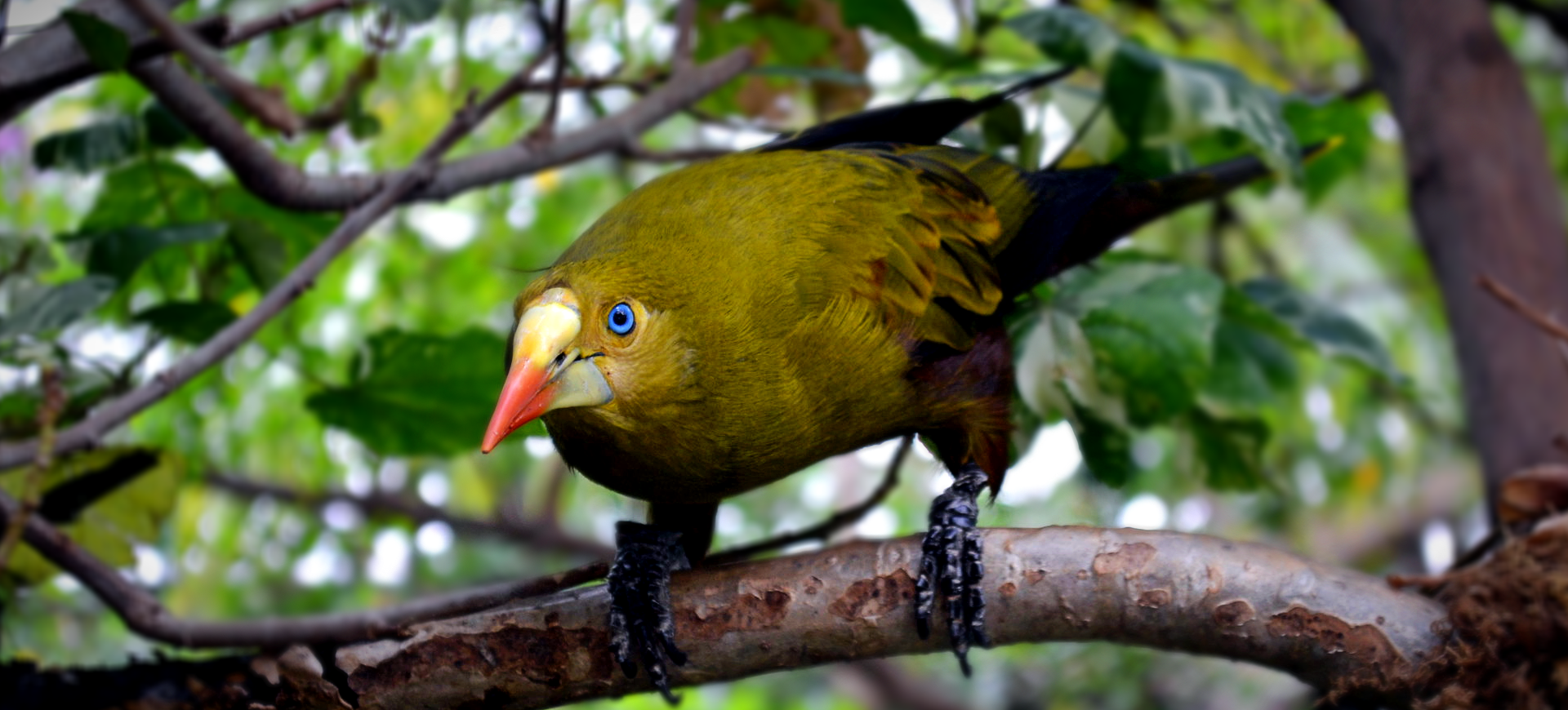
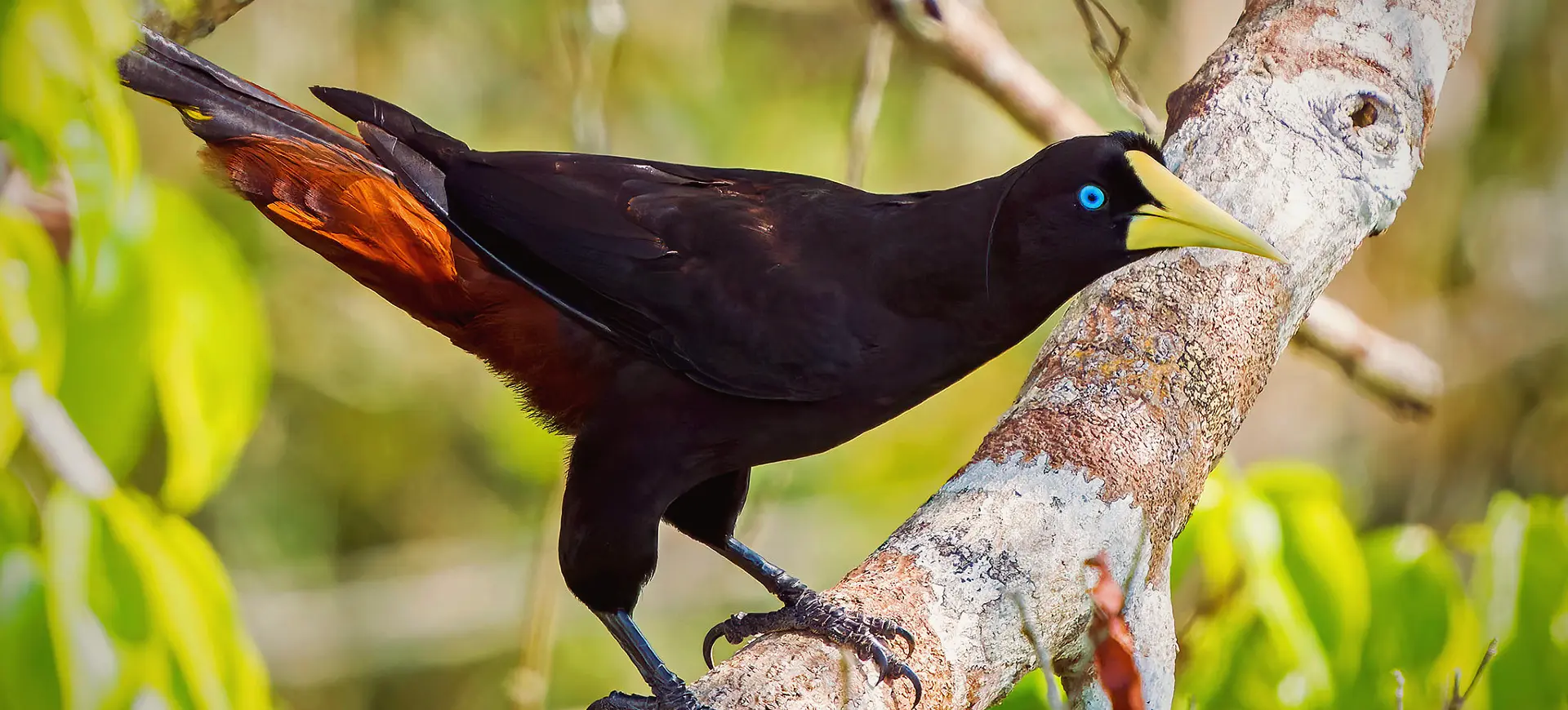
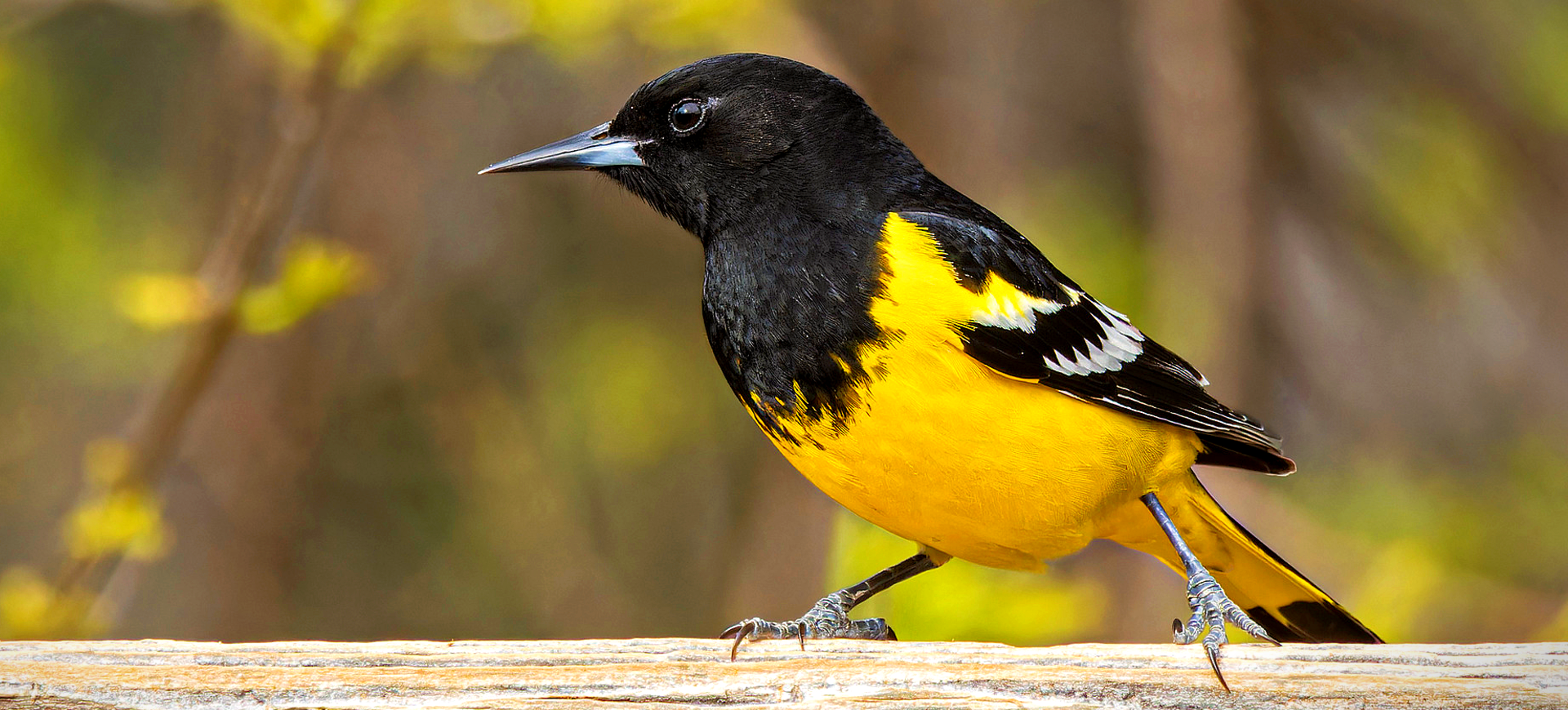
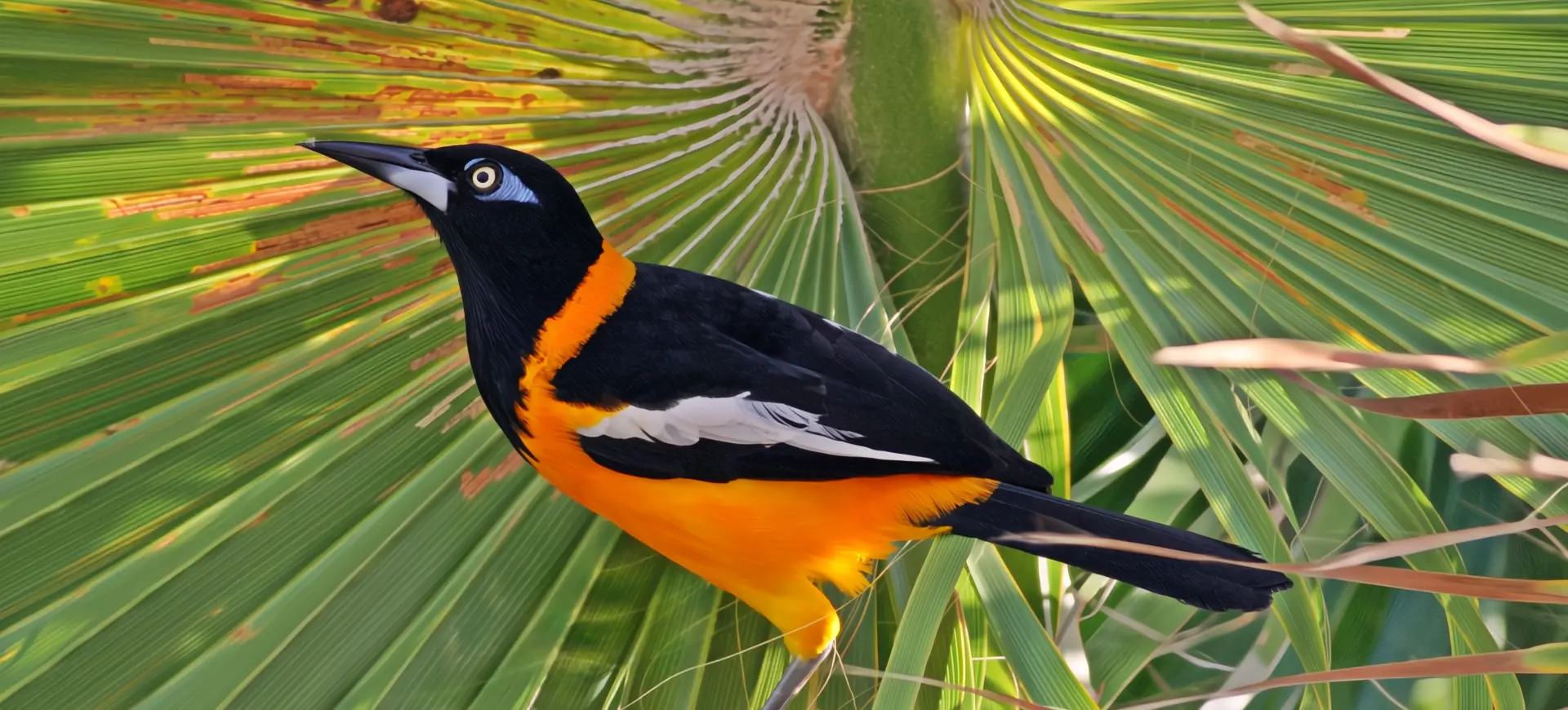
The Epaulet Oriole, scientifically known as Icterus cayanensis, is a vibrant bird species found in the tropical regions of South America. Its striking appearance is characterized by a bright yellow body, contrasting black throat, and distinct black and white wing patches, which resemble military epaulets, hence its name. These birds are part of the Icteridae family, known for their colorful plumage and melodic songs. Epaulet Orioles are medium-sized, with a slender build and a sharp, pointed beak that is adept at foraging for fruits and nectar and catching insects.
They inhabit various wooded environments, including tropical rainforests, savannas, and forest edges. The Epaulet Oriole’s adaptability to different habitats is a testament to its resilience and the breadth of its ecological niche. Their diet mainly consists of fruits and nectar, but they also consume insects, making them important for controlling pest populations and pollinating flowers. These birds are also known for their elaborate and musical calls, which they use to communicate with each other, especially during the breeding season.
Breeding pairs of Epaulet Orioles are often monogamous, with both males and females participating in nest-building and caring for their young. Their nests are typically constructed in the shape of a deep pouch or basket, suspended from tree branches, protecting from predators. This species plays a vital role in their ecosystems, not only as pollinators and pest controllers but also as seed dispersers, contributing to the health and regeneration of their habitats.
Taxonomy
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Type
Current distribution:
Epaulet Orioles are widely distributed across South America, covering Venezuela, the Guianas, Brazil, Paraguay, and northern Argentina. Despite facing habitat loss in some areas, they remain relatively common within their range, thanks to their adaptability to different environments. These birds are most frequently observed in regions with abundant flowering plants and trees, which provide the nectar and fruit that form the basis of their diet.
Their populations are generally stable, but continuous monitoring is necessary to preserve their habitats, especially in areas undergoing rapid development and deforestation. Efforts to maintain and restore their natural habitats are vital for the long-term conservation of Epaulet Orioles, allowing them to continue playing critical roles in ecosystem health and biodiversity.
Physical Description:
The Epaulet Oriole is easily recognizable by its bright yellow or golden body, with striking black markings around the throat and upper chest. The most distinctive feature of this species is the black and white patches on their wings, reminiscent of epaulets, which are particularly visible during flight. These birds possess a slender figure, with long legs and a straight, pointed bill perfectly adapted for their omnivorous diet. Both males and females share similar plumage, which aids in camouflage among the foliage, while juveniles display a more muted coloration until they mature.
Their physical attributes, including their vibrant plumage and agile flight capabilities, make them captivating sights in their natural habitats. Epaulet Orioles are medium-sized birds with a sleek and aerodynamic body shape that facilitates their acrobatic flying and foraging behaviors. The contrast between their yellow bodies and the darker surroundings of their habitat highlights their presence in the lush landscapes they inhabit. Observing these birds, especially in flight or actively foraging, provides a glimpse into tropical avian species’ dynamic and colorful world.

Lifespan: Wild: ~10 Years || Captivity: ~12 Years

Weight: Male: 1.2-1.4 oz (34-40 g) || Female: 1.1-1.3 oz (31-37 g)

Length: Male & Female: 7.1-7.9 in (18-20 cm)
Characteristic:
Native Habitat:
Epaulet Orioles are native to South America and thrive in diverse wooded habitats, from dense tropical rainforests to open savannas and forest edges. They show a particular affinity for areas with abundant flowering trees and shrubs, which provide essential resources for their diet and nesting. Their ability to adapt to various habitats has enabled them to occupy a wide geographical range, extending from Venezuela and the Guianas south through Brazil, Paraguay, and northern Argentina.
The presence of water bodies, such as rivers and lakes, within these habitats is also beneficial for the species, as these areas tend to support a rich diversity of insect life and vegetation. Conservation of their natural habitats is crucial for the survival of Epaulet Orioles, as habitat destruction and fragmentation pose significant threats to their populations. Protecting these environments ensures not only the well-being of this species but also the health of the broader ecosystems they inhabit.
Climate Zones:
Biogeographical Realms:
Continents:
Diet:
Diet & Feeding Habits:
The Epaulet Oriole has an omnivorous diet that primarily includes fruits, nectar, and insects. Their preference for nectar and fruits makes them important pollinators in their ecosystems as they move from flower to flower, facilitating the transfer of pollen. When consuming nectar, they prefer flowers with long corollas, using their slender beaks to access the sweet fluids. Insects, including beetles, caterpillars, and spiders, constitute a significant portion of their diet, especially during the breeding season when the demand for protein increases.
These birds are adept foragers, utilizing their agility and sharp beaks to extract food from various sources. They can often be seen hanging upside down on branches or fluttering mid-air as they forage, displaying their acrobatic skills. The Epaulet Oriole’s feeding behavior highlights its role in controlling insect populations and dispersing seeds, contributing to the biodiversity and health of their habitats. Its adaptability in diet and foraging methods allows it to thrive in a wide range of environments.
Mating Behavior:
Mating Description:
Epaulet Orioles are known for their monogamous mating system, where pairs form strong bonds and collaborate in nest-building and raising their young. The breeding season is marked by the males’ vibrant displays and melodic songs to attract females and defend their territory. Both sexes skillfully construct nests, woven into deep baskets or pouches suspended from tree branches, protecting the eggs and chicks from predators.
Parental care is a shared responsibility, with both males and females participating in feeding and guarding their offspring. This cooperative approach to reproduction ensures a higher survival rate for the chicks and exemplifies the strong pair bonds formed between mating partners. The Epaulet Oriole’s reproductive behaviors, including their elaborate nests and the mutual care of the young, highlight the complex social structures and adaptive strategies contributing to their success as a species.
Reproduction Season:
Birth Type:
Pregnancy Duration:
Female Name:
Male Name:
Baby Name:
Social Structure Description:
Epaulet Orioles exhibit a social structure characterized by monogamous pairs and family groups. During the breeding season, pairs work together to build nests and care for their offspring, demonstrating strong pair bonds and cooperative behavior. Outside the breeding season, these birds may gather in small flocks, especially in areas with abundant food sources, showcasing social interaction and community.
The species’ social dynamics, including pair bonding, cooperative nesting, and flocking behavior, illustrate the complexity of their interactions and the importance of social connections for survival and reproductive success. The Epaulet Oriole’s social structure is a fascinating aspect of their biology, reflecting the adaptability and diversity of avian life in tropical ecosystems.
Groups:
Conservation Status:
Population Trend:
The Epaulet Oriole is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN, indicating a stable population trend across its extensive range in South America. They are relatively common in many parts of their distribution, particularly in habitats undisturbed by human activity. The species’ ability to adapt to various environments has been crucial to its resilience, allowing it to maintain healthy populations even in areas experiencing habitat change.
Conservation efforts are focused on preserving the natural habitats of Epaulet Orioles, with an emphasis on protecting regions of ecological importance and preventing deforestation. Public awareness and education about the species and its role in the ecosystem are also key components of conservation strategies. Ensuring the preservation of their habitats will be essential for the continued stability of Epaulet Oriole populations and the overall biodiversity of their regions.
Population Threats:
The main threats to the Epaulet Oriole include habitat loss and fragmentation, primarily due to deforestation for agricultural expansion and urban development. These activities reduce the availability of suitable nesting sites and food sources, potentially impacting the species’ population numbers and distribution. Additionally, pesticide use in agricultural areas can decrease insect populations, an important part of their diet, further threatening their survival.
Climate change also poses a risk, as alterations in weather patterns and temperatures can affect the availability of resources and the timing of breeding seasons. Conservation efforts to mitigate these threats are crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of Epaulet Orioles and the ecosystems they support.
Conservation Efforts:
Conservation initiatives for the Epaulet Oriole focus on habitat protection and preserving biodiversity within their range. Efforts include establishing protected areas, reforestation projects, and sustainable land-use practices that minimize environmental impact. Education and community involvement play significant roles in these efforts, raising awareness of the importance of conserving natural habitats and the species that depend on them.
Collaboration between conservation organizations, governments, and local communities is essential for effectively protecting Epaulet Orioles and their habitats. By promoting the conservation of tropical forests and other critical environments, these initiatives contribute to preserving biodiversity and the health of ecosystems across South America.
Additional Resources:
Fun Facts
- Epaulet Orioles are named for their distinctive wing patches resembling military epaulets. These patches feature striking black-and-white contrasts against their bright yellow bodies.
- They construct unique hanging nests woven into deep baskets or pouches and suspended from tree branches to protect against predators.
- This species is known for its musical and complex songs, which males use to attract mates and communicate territorially.
- Epaulet Orioles play a crucial role in their ecosystems as pollinators and seed dispersers, aiding in the growth and spread of tropical forest flora.
- Despite their vibrant plumage, they can be difficult to spot in their natural habitat, blending seamlessly into the foliage and dappled sunlight of the forest canopy.
- They have a versatile diet, feeding on fruits, nectar, and insects, showcasing their adaptability to different food sources.
- The strong pair bonds formed between monogamous Epaulet Oriole partners are essential for their breeding success and cooperative parenting.
- Not commonly found in captivity, Epaulet Orioles are most often admired in their natural settings, where they contribute to tropical forest biodiversity.
- Their omnivorous diet and foraging behavior have significant ecological impacts, including controlling insect populations and facilitating plant reproduction.
- Conservation efforts for Epaulet Orioles emphasize habitat preservation, highlighting the importance of tropical forest conservation for maintaining biodiversity.