- The Giant Panda’s diet primarily consists of bamboo, affecting its ability to hibernate.
- Bamboo’s low nutritional content means pandas cannot store enough fat for hibernation.
- Instead of hibernating, pandas migrate to lower elevations during winter.
- Panda conservation is crucial due to their limited habitat and declining numbers.
- Conservation efforts involve habitat protection, breeding programs, and public awareness.
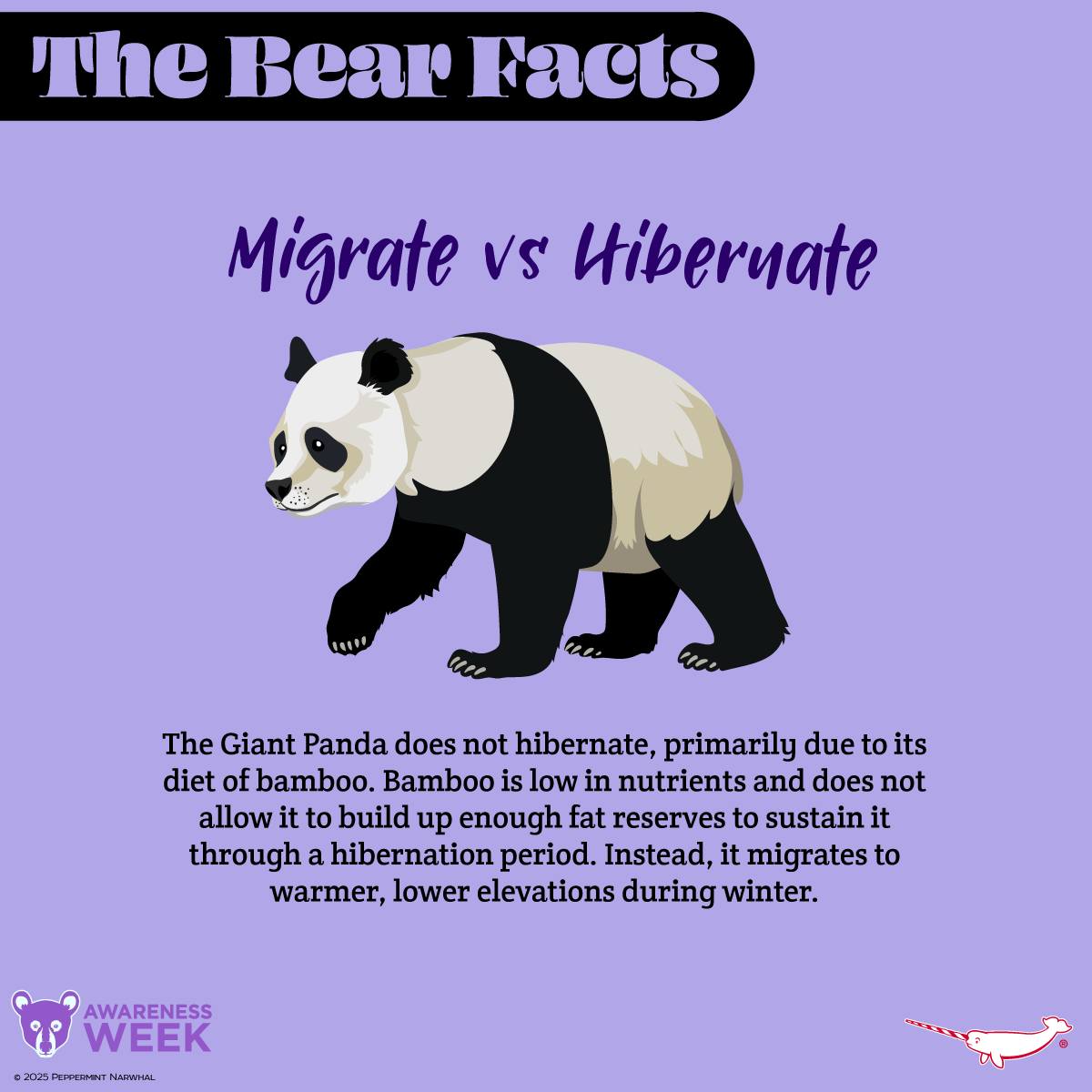
The Giant Panda, a beloved symbol of wildlife conservation, is notable for its distinct characteristics and unique behavior. Unlike many other bear species, the Giant Panda does not hibernate. This is primarily due to its exclusive diet of bamboo, a factor that significantly influences its survival and lifestyle choices.
Bamboo comprises roughly 99% of a panda’s diet. While bamboo is abundant in the pandas’ natural habitat, its nutritional profile lacks sufficient calories and nutrients. Pandas consume between 26 and 84 pounds of bamboo daily to meet their energy needs. Despite this high intake, the nutritional shortages in bamboo prevent pandas from building the fat reserves necessary for hibernation, unlike bears that consume energy-rich foods like nuts and berries to prepare for winter dormancy.
This dietary limitation means that instead of retreating to a den to wait out the cold season, pandas must remain active throughout the year. To cope with the frigid temperatures, pandas migrate to warmer, lower elevations during the winter months. This migration helps them maintain access to bamboo-rich areas and avoid the harsher conditions of higher altitudes. This adaptation showcases their resilience and unique adaptations to their environment.
The impact of diet on the Giant Panda’s lifestyle highlights the complex relationship between an animal and its habitat. The panda’s existence is intricately linked to the availability of bamboo, making habitat conservation efforts crucial. These efforts aim to ensure that bamboo forests are protected and that pandas have the continuous food supply they need to survive.
Panda conservation is a multifaceted challenge, driven by their endangered status and the limited range of bamboo forests. Deforestation and habitat fragmentation pose significant threats to their survival. To mitigate these risks, global conservation programs focus on preserving natural habitats, promoting sustainable development, and implementing reforestation projects.
Breeding programs play a vital role in ensuring the Giant Panda’s survival. Pandas have a notoriously low birth rate, with females ovulating just once a year. Captive breeding initiatives aim to increase the population by facilitating successful breeding encounters and providing a safe environment for cubs to thrive. These programs rely on scientific research to improve breeding success rates and genetic diversity.
Public awareness is essential in driving conservation efforts. International campaigns and educational programs help increase understanding of the challenges facing the Giant Panda and foster a sense of responsibility toward wildlife conservation. Engaging global communities in these efforts encourages support and funding, vital for ongoing preservation initiatives.
Merchandising and fundraising also contribute to conservation. Organizations sell bear-themed merchandise, such as enamel pins and other collectibles, to raise money for panda conservation projects. These sales provide a meaningful way for individuals to support efforts while raising awareness through tangible items that spark conversation.
During Bear Awareness Week, for example, supporters have the chance to engage with information about bears, including the Giant Panda, and contribute to conservation efforts. Promotions such as sales and crowdfunding campaigns offer opportunities for the public to get involved financially, ensuring continuous support for endangered species initiatives.
International trade regulations play a protective role too. Restrictions on bamboo harvesting and land use in panda habitats are designed to create a sustainable balance between human activity and wildlife conservation. These regulations are crucial in maintaining healthy ecosystems that support not only pandas but a diverse array of plant and animal life.
In summary, the Giant Panda’s reliance on bamboo dictates its inability to hibernate, compelling it to migrate in search of food and milder conditions. Conservation efforts are vital for ensuring this iconic animal’s future, requiring a collaborative approach involving habitat protection, breeding programs, and global awareness initiatives. Effective conservation is a testament to humanity’s dedication to preserving the natural world and safeguarding its inhabitants for future generations. Through understanding and supporting these efforts, we play a part in the ongoing narrative of wildlife conservation.
*****
Source Description
The Bear Facts – The Giant Panda does not hibernate primarily due to its diet of bamboo. Bamboo is low in nutrients and does not allow it to build up enough fat reserves to sustain it through a hibernation period. Instead, it migrates to warmer, lower elevations during winter.
BEAR MERCH: https://www.peppermintnarwhal.com/s/search?q=bear
Happy Bear Awareness Week!
This completes our Bear Awareness Week. Let us know what you thought of this year’s celebration in the comments.
FINAL WEEK TO PLEDGE!
Kickstarter – Endangered 7!
PLEDGE NOW: pnpins.com
Campaign ends May 28, 2025.
We appreciate the support!
SALE – Save 15% on ALL Endangered & Frog enamel pins thru May 31, 2025.
Shop www.peppermintnarwhal.com
International Shoppers (outside of the USA and Canada) visit our store on Etsy:
www.etsy.com/shop/PeppermintNarwhal